What is Financial Services ?
Financial services are the services which are offered by the financial companies. The financial companies comprise of both Asset Management Companies and Liability Management Companies. In Asset Management Companies, there leasing are companies, mutual funds, merchant bankers and issue/portfolio managers while Liability Management Companies has the bill discounting and acceptance houses.
In other words, the financial service is referred to as the products and services which are offered by the banks as they provide various kinds of facilities of financial transactions and other financial activities loans, insurance, credit cards, investment opportunities and money management and also give information on the stock market and other issues like market ups and downs. The basic aim of this sector is to act as intermediary between individual and institutional investors which will help in financial transactions.
Definition of Financial Services
The financial service industry is defined as, "The collection of organizations which intermediate and facilitate financial transactions of individual and institutional investors from their resource allocation activities through time".
Thus, the financial services comprise of various works related to change of savings into investment.
Objectives of Financial Services
The various objectives of financial services are as follows :
1) Fund Raising :
The required funds can be raised by the help of financial services from the host of investors, individuals, institutions and corporate. There are various instruments of finance being used for raising funds. These kinds of funds are required by the corporate houses, individuals, etc.
2) Funds Deployment :
There are various kinds of financial services present in the financial markets which help the company in proper deployment of funds. It also helps in decision-making of financial mix. The financial service provide various types of services like bill discounting, factoring of debtors, shifting of short-term funds in the money market, credit rating, e-commerce and securitization of debts for effective funds management.
3) Specialized Services :
The various specialized services are being provided by financial service except banking and insurance like credit rating, venture capital financing, lease financing, factoring, mutual funds, merchant banking, stock lending, depository, credit cards, housing finance, book-building, etc. These services are provided by various kinds of institutions and agencies like stock exchanges, specialized and general financial institutions and non-banking finance companies, subsidiaries of financial institutions, banks and insurance companies. etc.
4) Regulation :
There are various kinds of regulatory bodies present in India like Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Department of Banking and Insurance of the Government of India which have different types of legislation's and also help in providing various kinds of functions of financial services institutions.
5) Economic Growth :
The financial services help in increasing the economic growth and development of country. It is done by the help of mobilizing the saving of the public by investing in productive investments. Due to this reason, the various developed and developing countries which are engaged in the effective financial market has increased the savings and investments.
Scope of Financial Services
The scope / functions of financial service is as follows :
1) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) :
The gross domestic product refers to the financial value of all the finished goods and services manufactured inside the country in a specific time period. The financial service contributes to the GDP of the country.
2) Employment :
The financial service requires various kinds of financial institutions which need different kinds of skilled manpower which indirectly lead to increase in the employment of the country.
3) Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) :
The financial service helps in increasing the foreign direct investment in the country which helps in increasing the growth of the country.
4) Mobilizing of Funds :
The financial service helps in increasing the investment opportunity among the public leading to mobilizing the funds of the public.
5) Long-Term Loan :
The long-term loan is basically required by the industries. The financial service helps in providing cheap and long-term loan to industries.
6) Insurance :
There are various types of financial services. Among them the most important is insurance. The insurance financial protection to the consumers.
Nature of Financial Services
The nature of financial services are given below :
1) Intangibility :
The financial services are intangible in nature. The companies need to build goodwill and confidence in the clients for producing better and efficient financial services. The quality and innovations plays an important role for building reliability among the customers.
2) Customer Orientation :
The financial institution selling financial services needs to study the demand of the customers. By the help of various studies, the financial institutions makes different strategies relating to the costs, liquidity and maturity consideration of the financial products. Hence, financial services are customer-oriented.
3) Inseparability :
The financial institutions and its customers cannot be separated from each other while producing and supplying of financial services as both the functions of financial service is done at the same time.
4) Perishability :
Financial services cannot be stored as they need to be created and delivered to the target customers as per their requirements. So, it is important for financial institutions to assure that there is match of demand and supply of financial services.
5) Dynamism :
The financial service should be dynamic so that they can be changed according to the socio-economics changes in the economy like disposable income, standard of living, level of education, etc. The financial services should be efficient so that the new services can be made by studying the future wants of the marker.
6) Derivatives and Catalysts :
The financial services are derivatives of financial market. So, they also act as a catalyst in the market operation. It starts the market operations and help in increasing the investment by increasing the saving for a high rate of capital formation. They help in various financial products which are derived from various financial transactions.
7) Act as Link :
The financial services bridge the gap between investors and borrowers. They give profit bearing investment to the investors by which they can also minimize the risk. The investors have the options of high risk and high profits, low risk and low profit or get a regular income on acceptable risk. The borrowers are also given many financial services for fulfilling the financial needs by lowering the cost of funds and also making the repayments according to the income pattern.
8) Distribution of Risks :
The financial services distribute the funds in the profitable manner so that the investors can diversify their risk in different financial services for getting maximum rate of return. The various experts in the market help the investors for proper selection of the portfolio for getting maximum return.
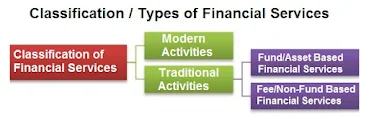
Types of Financial Services
The financial services are divided into wholesale financial service and retail financial services according to the profile of users.
The wholesale financial services are the services which are used for converting into final retail products. It is used by industry and business people. The retail financial services are given to the individual for direct consumption. The Classification of Financial Services are as follows :
Traditional Activities
The financial intermediaries from the past are providing various services including the money and capital market activity. The traditional activities are classified into fund based activities and non-fund based activities. These are also known as assets based financial services and fee based financial services respectively.
Fund/Asset Based Financial Services
In this, the financial services are used for making assets or are backed by assets in which the funds are changed to assets which are known as asset based financial services. It consists of the following :
1) Lease Financing :
A lease is known as the agreement between two parties known as lessor and lessee. The lessor is the owner of the asset and lessee is the user of the asset. In this agreement, there is transfer of asset from lessor to lesser for certain time period, in return the lessor receives the regular rent. As the lease period gets over, the asset is returned back to lessor until there is renewal of the contract.
2) Hire Purchase :
The hire purchase refers to the hiring of an asset for certain time period and when the time period gets over, there is purchase of same asset. At the time of sharing of asset, the person hiring the asset gets the ownership and is allowed in use it. It is being used for financing of capital goods like industrial finance, financing of consumer goods and for selling consumer good on hire purchase as it is a legal advice.
3) Factoring :
Factoring is done when the company requires immediate money. It is done by selling the account receivable like invoices to a third party known as factor at certain discount for immediate cash. This cash is required for continuous working of the business.
4) Forfeiting :
Forfeiting is the way of financing of receivable related to international trade. It represents to the purchase done by bank and financial institutions of trade bills/promissory notes instead of recourse to the seller. The purchase is done by discounting the documents including the overall risk of non-payment in collection. The various problems related to collection are accountability of the purchaser who pays cash to seller after discounting the bills and notes.
5) Mutual Fund :
Mutual fund is the type of investment in which the pool of funds is sourced from various investors for investing in various securities like stocks, bonds, money market instruments and similar assets. It is managed by the money managers who invest the fund capital and tries to get capital gains and income for the investors of the fund. The portfolio of mutual fund is organized and is according to the investment objective given in the prospectus.
6) Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) :
It is traded same like stocks in the stock exchange. It has the following assets like stocks, commodities or bonds. They trade near to the net asset value according to the working of the trading day. The ETFs also has a role to monitor various index like stock index or bond index. Exchange traded funds is useful for investments as there are low costs, tax efficiency and stock-like features. They are very famous among exchange-traded product.
7) Consumer Credit/Consumer Finance :
The term consumer credit means the activities related to giving credit to the consumers for empowering them to acquire their own goods required for daily use. It is also known as credit merchandising, deferred payments, installment buying, hire purchase, pay-out-of income scheme, pay-as-you earn scheme, easy payment, credit buying, installment credit plan, etc.
8) Bill Discounting :
The bill discounting or a bill of exchange is known as the short-term, negotiable and can easily liquidates money market instrument. It is used for financing a transaction in goods which is trade related instrument.
9) Housing Finance :
The housing finance refers to the collection of all the financial arrangements which are offered by the Housing Finance Companies (HFCs) for fulfilling the need of housing.
10) Venture Capital :
Venture capital includes two words i.e. venture and capital Venture refers to the way of doing something whose result is not known as it is present with various kinds of loss while capital refers to human and non-human resources required for starting the business.
Fee/Non-Fund Based Financial Services
The fee based financial does not provide instant fund but instead it allows for the creation of funds by the fee charged service. It consists of the following :
1) Merchant Banking :
The merchant banker can be individual or institutions like an underwriter or agent for the companies and municipalities allocating securities. They are also involved in broker or dealer functions, maintain the market for previously issued securities and also gives suggestion to the investors on the advisory services. It plays important part in mergers and acquisitions, private equity placements and corporate restructuring.
2) Credit Rating :
The credit rating is the process in which the symbol is assigned to the instrument for some special work which is referred to as benchmark of present knowledge on related capacity on the issuer to service its debt obligation on particular time. The symbols used in credit rating are basically alphabetical or alphanumeric. The comparison of different instruments is easy by the help of credit rating. The basic objective of credit rating is to inform the investors about the relative ranking of the default-loss probability for required fixed income investment in comparison to other rated instruments.
3) Stock Broking :
The stock broking refers to the method of bringing together the buyers and sellers of stock at the stock exchange. It is the function of financial service intermediary. It is done by brokers, both main brokers and sub brokers who are allowed by the SEBI. The stock broker can be individual broker, a firm of brokers or a corporatized broker.
4) Securitization :
The change of present or future cash inflow of an individual into trade-able security which can be sold in the market is known as securitization. These cash inflows can be from financial assets like mortgage loans, automobile loans, trade receivables, credit card receivables, fare collections will be security according to which borrowing can be raised. Though an individual can take the assistance of securitization instruments for efficient economic growth.
5) Letters of Credit (LC) :
A letter of credit is issued by the bank of the buyer to the seller which has a written undertaking for repaying the cost of goods and services given by the seller to the buyer in place of producing documents required within the precise time, place and to prescribed bank as stated in the documents which is submitted according to the terms and conditions of the LC.
6) Bank Guarantees :
The guarantee is the contract between the issuing bank and the client in which the bank attempt to take the claims presented by the client on the customer on behalf of which the bank had guarantee. The payment of default can be taken from the bank by the client in case the customers do not fill the obligation. The bank is only liable for the amount declared in the contract if the amount of default is more than the bank will have to give the whole amount.
Modern Activities
The financial intermediaries also have other services besides the traditional services. These are of non fund based activity. These are classified under New Financial products and services. The different services are as follows :
- It provides various project advisory services starting from the preparation of the project report until raising of funds along with the various government approvals.
- The planning and implementing the process involved in for merger and acquisition.
- It assists the corporate customers in capital restructuring.
- It acts s the trustees to the debenture holders.
- It helps in achieving the better outcome by giving required changes in the management structure and management style.
- It help helps in finding the better joint venture partners and also making the joint venture agreements which directly help in structuring the financial collaborations and joint ventures.
- It also helps the sick companies by rehabilitating and restructuring the proper plans in the execution of the scheme.
- It helps in reducing risk by the help of exchange rate risk, interest rate risk, economic risk and political risk by using swaps and other derivative products.
- It It helps in controlling the portfolio of large public sector company.
- It is involved in risk management service like insurance services, buy-back options etc.
- It also gives suggestions to clients on the way of choosing the better source of funds by taking up the various funds, cost, lending time, etc.
- It also helps the client in lowering the debt cost and also for selecting the better optimum debt equity ratio.
- It also helps the companies which are related in credit rating and want to go public by the issue of debt instruments.
- It takes the various services associated to the capital market like :
- Clearing services
- Registration and transfers
- Sate custody of securities
- Collection of income on securities
Regulatory Framework of Financial Services
Usually, the regulatory framework has the objective of establishing the efficient and effective financial institutions and also assists in maintaining the stability of the transmission method and also safeguarding the consumers of the financial services. The regulatory framework of financial services in India is shown below :
1) Framework for Banking and Financing Services :
The banks handle two functions which also determine their growth. These functions are savings and investments. The working of the banking and financial institutions is controlled by Central Government and RBI. The central government and RBI help in maintaining the growth of economy according to the requirement. The RBI by the help of RBI Act and Banking Regulation Act controls all the financial institutions which are related to saving and capital formation. There are various other laws for institution which are involved in raising and lending the capital. The various regulations for banking institutions are as follows :
i) New Branch :
It gives permissions for establishing new bank or new branch.
ii) Capital :
It suggests the minimum capital, reserves and need of profit and reserves, dispersion of dividends, the amount requirement for minimum cash reserve and other liquid assets.
iii) Inspection :
The proper monitoring and maintenance on the functioning of the banks.
iv) Appointment :
The various appointments of Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of private banks and nominating members to the Board of Directors done.
v) Monetary Policy :
The planning and implementation of monetary and credit policy for effective regulation of credit flows. Maintenance of certain amount by t deciding Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR). The various treasury operations are done by the regular issue of bonds and repos.
vi) Credit Control :
The various qualitative and quantitative credit control method are used for managing credit flow to different industries.
vii) Other Services :
The various other services like regulating, factoring, bill discounting and credit card services are offered by the banks.
2) Framework for Insurance Services :
The Insurance Act, 1938 was made for managing the insurers prior to the nationalization of life and general insurance. The LIC formed in 1956 and GIC was formed in 1973 are the big institutions in insurance service. The nationalization of the insurance companies has changed the working of the Act. The regulatory functions came along with LIC and GIC.
The RBI appointed the Malhotra Committee in 1993 for providing ways to enhance the functioning of various insurance services present in India so the Insurance Regulatory Authority (IRA) was framed in 1996. The IRA performs the following works for both public and private insurance company :
i) Orderly Growth :
The regulation and promotion of the insurance business leads to the orderly growth.
ii) Exercise of Powers :
The various powers and functions of the controller of Insurance under the Insurance Act, 1938, LIC Act, 1956 and the General Insurance Business (Nationalization) Act, 1972 or any other law relating to insurance in force at the time it is exercised and performed.
iii) Protecting Policy-Holders :
The various interest of policy-holders like assigning of policy nomination by policy-holders, insurable interest, settlement of insurance claims, surrender value of policy and other terms and conditions of contract insurance, besides controlling and regulating the rates. advantageous terms and conditions that are offered should be protected by the insurer.
iv) Professionalization :
The professional organization related to the insurance business should be controlled and promoted.
v) Information :
The various information of the inspection, inquiries and investigation including audit of the insurers, insurance intermediaries and other organizations related to the insurance business can be called by the governing body.
vi) Books Maintenance :
The way of maintaining the books of accounts with all the statements of accounts is prescribed to the insurers and other insurance intermediaries.
3) Framework for Investment Services :
The various fund-based activities like mutual funds and venture capital is related to the investment services. In the same way, the stock exchange and stock broking institution is also related with the investment activities. The regulations followed by them can be discussed with other investment activities. The Securities Contracts (Regulations) Act (SCRA), 1956. SEBI Regulations and Reserve Bank of India comprises of the regulatory is defined.
4) Framework for Merchant Banking and Other Services :
The working of different types of intermediaries related to the management of public and right issue of capital, like merchant bankers, underwriters, brokers, market-makers, registrars, advisors, collection bankers, advertisement consultant, debenture trustees, credit rating agencies etc., are controlled by various guidelines of SEBI which are explained as follows :
- SEBI (Merchant Banker) Regulation, 1992
- SEBI Rules for Underwriters
- SEBI (Brokers and Sub-brokers) Regulation, 1992
- SEBI Rules for Registrars to an Issue and Share Transfer Agents, 1993
- SEBI (Bankers to an Issue) Regulations, 1994
The regulations for merchant bankers and other intermediaries are as follows :
- The business should be registered with SEBI prior to the commencement of business according the related rules and to regulations.
- The various rules and certification relating to the net-worth, capital adequacy and code of conduct should be followed.
- The proper monitoring of the books and records should be done and also various investigations should be done on the working of intermediaries. The accurate measure should be suggested wherever required.
- All the guidelines of SEBI should he followed and the "due-diligence certificate" should also be issued.
- The SEBI guidelines for Disclosure and Investor Protection, 1992 related to the issue of capital and SEBI (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeover) Regulations, 1994 related to the method to be followed by the acquirer and the merchant banker for such acquisition of shares should be followed.
Reasons for Regulation of Financial Services
The reasons for the regulation of financial services are as follows :
- The market efficiency can be improved.
- It helps in removing the illegal trade practices.
- It helps in maintaining the transparency in the operation and avoiding the case of manipulation.
- It helps in increasing equality and correctness.
- It also helps in safeguarding the small investors, depositors, insurance policy holders and securities investors.
- It helps in avoiding the misconduct in the market.
- It helps in maintaining the stability of the financial system.
- It helps in taking decisions regarding the plans and policy of financial system.
- It helps in representing the international platform which helps in increasing the coordination with the international financial administration policy.
- It checks that the working is done according to the rules concerned with the financial markets.
- It manages the financial regulation by issuing orders of cancellation or termination of licenses forcing disciplinary sanctions, instructing corrective methods, etc.
- Establishing the capability of financial service providers.
- It helps in providing confidence in the financial system.
- It reduces the breaching of laws.
Importance of Financial Services
The advantages of financial services are as follows :
1) Economic Growth and Development :
The financial service is very important for economic growth and development. The banking, saving and investment, insurance and debt and equity provides help both to the private citizens and business. The private citizens get help in saving money, getting protection against some causalities while helps the business in their formation, increasing the efficiency and also for expanding the business both nationally and internationally. It also helps the poor section of societies as these services helps in lowering the vulnerability and helping people to control the availability of assets for making the income and options which leads to poverty in the society.
2) Contribution in GDP :
The financial service sector has the largest earning which consists of various type of business like merchant banks, credit card companies, stock brokerages and insurance companies. It is largest in the world. The financial services contribute a larger part of GDP.
3) Promotion of Liquidity :
The basic feature of the financial service is to use the money and monetary assets for producing the goods and services so for this process there the requirement of regular flow of money. The money and monetary assets are referred to as the liquidity in finance. While liquidity can also be known as the money and other assets which can be changed into cash and reduce the risk of loss.
4) Generate Employment :
The financial service also helps in generating employment in the country as it is in the growth stage. It is helpful for the developing country like India. It also helps in expanding the financial market. It helps in increasing the FDI flow in the country which is required for the growth of the country.
5) Link between Savers and Investors :
The financial service helps in bridging the gap between the depositors and investors which helps in increasing the savings and investments. It helps in doing proper allocation of resources which help in mobilizing the saving of the public. It also contributes in the continuous up-gradation of the technology. These all factors have increased the growth of the country on the sustainable basis.
6) Reduce Cost of Transaction and Borrowing :
The financial services has helped in making such financial structure which has the lower cost of transactions. It has increased the profit on the return to the savers and it also lowers the cost of borrowing which increases the rate of saving among the people. The financial services also help in providing the cheap and long-term loans to different industries.
7) Minimizes Situations of Asymmetric Information :
The various financial services like insurance, pension and portfolio adjustment helps in providing the financial protection and reducing the conditions in which the information is not regular and may also affects the performance of the operators or when one party has the details while the other does not have.
8) Financial Deepening and Broadening :
The financial services helps in developing the process of financial deepening and broadening. Financial deepening means increasing the financial assets according to the percentage of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Financial broadening means in increasing the number of financial assets and also the variety of participants and instruments.
9) Helps in Projects Selection :
The financial services also help in improving the performance of the investment. It also helps in providing the way for exchanging the goods and services and also transferring the economic resources by time and also geographic region and industries.
10) Allocation of Risk :
The financial service works in doing optimum allocation of risk bearing. It reduces, merges and trade various kind of risks which is used in mobilizing the saving and assigning the credit. The financial services work to make the risk within the limits and also reduces the gathering cost and examining the information to help the operators in decision making.
Limitations of Financial Services
The growth rate of financial service is very fast but they also face some issues and problems. These financial services face various challenges for accomplishing the financial demand of the economy. The various disadvantages of financial services are as follows :
1) Lack of Qualified Personnel :
The financial services sector requires the financial creativity. There is lack of qualified and trained employees to do so. It also reduces the growth of the economy.
2) Lack of Investor Awareness :
The investors do not have knowledge about the new financial products and instruments which makes it of no use and the investors also does not get the advantages of innovative products and instruments.
3) Lack of Transparency :
As the financial system is expanding in various forms both national and international wise but do you the lack of transparency in keeping the accounts the growth of financial system is very slow.
4) Lack of Specialization :
There is lack of specialization in India as each financial intermediary trade in different financial service without having knowledge in one or two area While in other countries the financial intermediaries work only in those area in which they are specialized.
5) Lack of Recent Data :
The financial intermediaries are not involved in research work so they do not get any updated information which is important for doing any new innovation in the financial service.
6) Lack of Efficient Risk Management System :
Due to globalization of the economy the various multinational companies are entering the Indian market and importance is given to the foreign portfolio flows. There is flow of various kinds of currencies which increase the various kind of risk like exchange rate risk, interest rate risk, economic and political risk.
Growth of Financial Services in India
The various stages of growth/Evolution of financial services in India are as follows :
1) Merchant Banking Era :
The merchant banking era consisted of the period between 1960 and 1980. In this period, there was growth in various kinds financial services like merchant banking, insurance and leasing services. The functions of merchant banking are as follows :
- The project should be identified, the feasibility reports should be prepared and the detail project reports should be prepared.
- The various marketing, managerial, financial and technical analysis should be done on behalf of the customers.
- The accurate capital structure can be made by the help of merchant banking.
- It acts as the link between the capital market and the fund-seeing institutions.
- It helps in underwriting.
- It helps the companies in listing the issues on the stock exchange.
- It also suggests various ways of doing mergers and and acquisitions.
- It helps in giving technical suggestions on leveraged buyouts and takeovers.
- It helps in providing syndication ability by providing project finance.
- It helps in providing working capital loans.
2) Investment Companies Era :
In this era, there was introduction of various investment institutions and banks. These investment institutions comprise of the Unit Trust of India (UTI). Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) and the General Insurance Corporations. (GIC). The UTI is the largest public sector mutual fund in the world. The LIC is related with the life insurance business. It is a public monopoly. The various private insurance companies was nationalized in 1970. After the nationalization, the insurance company was made as the holding company which had four subsidiaries for managing the general insurance business in the public sector. At the end of 1970, the leasing business has come up. Earlier these companies were working on the equipment lease financing but now the leasing of various operations like financial, operating and wet leasing was done.
3) Modern Services Era :
During 1980, there was the introduction of financial products and services. The financial service consists of over the-counter services, share transfers, pledging of shares, mutual funds, factoring, discounting. venture capital and credit rating. The mutual fund industries for increasing the savings habit among the people introduced various innovative schemes for mobilization of savings. The mutual funds have the transparent asset and liability. management which help the investors in getting increased and constant return on the investment done by them.
The credit rating was the important financial service introduced by Indian financial sector. The introduction of the credit rating system was done for increasing the confidence of investors and also for increasing the participation in the capital market operations and also encouraging the better and effective financial discipline in the system. Another important advancement took place by preparing the structure of venture capital funds. The short-term financing for domestic and international trade was factoring. The introduction of commercial banks in financial service leads to the change in the financial system in India.
4) Depository Era :
There was the introduction' of depositories in this era for combining the Indian financial sector industry with the global financial service industry and for encouraging the paperless trading by the help of dematerialisation of shares and bonds. The trading in "Gilts" was permitted by Central Government in 1997-98 by introducing the Stock-Lending Scheme. It prepared individual department to deal with the trading of Gilts. Another method for establishing effective financial service sector in India is the introduction of book-building with the help of both the investors and fund users. The various online trading platforms were brought up by Bombay Stock Exchange, the Delhi Stock Exchange and the computerization of the National Stock Exchange. It will help in building the better financial service market in India.
5) Legislative Era :
There were various legislation's framed in this era for developing the financial service sector. The FEMA was replaced by FERA. The change was done by introducing the separate legislation for internet trading. There were amendments done in Indian Companies Act, Income Tax Act, etc., for increasing safe and better trading and clearing of transactions.
6) Foreign Institutional Investors Era :
The government introduced economic reform which is very important for the various participants. The disinvestment guidelines are given by SEBI in which the Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) are allowed to work in the Indian capital market. It is done for giving entry to the foreign investors in the Indian capital market and en-chasing the growth and development.