What is Factoring ?
The word 'Factoring' is derived from Latin word 'Factor' which denotes 'doer'. The definition of the word factor is "One that lends money to producers and dealers on the security of accounts receivables".
Factoring means a financial transaction which involves a firm selling its invoices of accounts receivables to a third party, which is also known as a 'Factor'. Such transfer is generally made at a discount and the firm is provided with the instant cash for financing its ongoing business.
Definition of Factoring
Alam Calpin has defined the term as :
"Factoring is a system designated to eliminate payment risk in overseas sales and ensure that the seller receives prompt settlements".
C. S. Kalyanasundaram defines the term as :
"Factoring is the outright purchase of credit approved account receivables with the factor assuming bad debt losses"
A factor is a financial institution which engages in the work of collecting account receivables of a business. Such financial institution takes the credit risk attached to such account. Factoring denotes selling of the receivables and it may be with recourse or without recourse. With this facility, a business is able to get quick cash for its operations. Following are the main elements of a factoring transaction :
- The Factor
- The Client (Seller)
- The Customer (Buyer)
The contract between the two parties determines these elements. Such contract is drawn for a fixed period of time and is generally renewable. The contract may also be cancelled by giving due notice.
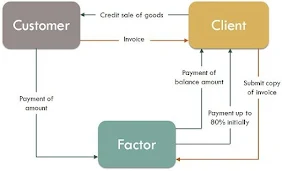
Process / Mechanism of Factoring
The basic service provided by a factor is the collection of proceeds. such cases, the factor offers its services as an intermediary between the buyer and the seller. Once a factor receives the payment, the firm's account is credited after making deduction for the services provided by the factor. The procedural facets of factoring may be explained using the following figures :
- The client orders goods or services on credit. Such services or goods are delivered along with the invoice.
- Client makes the assignment of the invoice to the factor.
- Factors may up to 80 percent of the value of the invoices as advance to the seller.
- The factor provides regular statement of accounts and follow-up.
- Customer pays the dues to factor.
- Factor makes the remaining payment to the client at the time of actual collection of the debt.
Types of Factoring
The main variations of factoring arrangements are featured below :
1) Recourse Factoring :
Under recourse factoring, the factor buys trade receivables and provides collection services. The factor is also responsible for maintaining the sales ledger. However, if payment is not made or default is incurred, then the client is responsible for making the good the loss for factor. Thus, no protection from bad debts is provided under this kind of arrangement. Such kind of arrangement is prevalent in developing countries.
2) Non-Recourse Factoring :
This type of arrangement denotes absolute responsibility for the factor. In such cases, the factor is not entitled to receive payments from the client for the debtors default. Such type of factoring is generally more expensive than Recourse Factoring as it provides protection to the client. against bad debts. Such type of arrangement is more popular in advanced economies.
3) Advance Factoring :
Such type of arrangement involves the payment of a pre-determined portion of the debt in advance. Such portion may range between 75 percent and 90 percent. Remaining is paid after the collection is made. The factor provides a drawing limit to the client immediately after the approval of the invoices The client is responsible for making interest payments for the period elapsed between the date of advance payment and the date of actual collection of the debt. Such interest rate is determined on the basis of several factors such as the duration and credit standing of the client.
4) Bank Participation Factoring :
This is a type of advance factoring. This type involves a bank offering an advance to the client for financing a portion of the factor reserve, which is the difference between the factor debt and the advance provided by the factor. For For example, if the factor extends an advance of 40 percent and the bank makes another advance of 30 percent of the debt, then client will only have investment of 30 percent in the debt as the remaining is provided by the factor and the bank.
5) Maturing Factoring :
This type of factoring is also known as Collection Factoring. No pre payment is made by the factor to the client under this kind of arrangement. The payment is made on the date guaranteed payment date. Alternatively, payment may also be made on the date of collection.
6) Notified and Undisclosed factoring :
Under such kind of factoring arrangement, the debtor is notified that their debt has been assigned to the factor. They are also advised to make the payment to the factor instead to the firm. Under Undisclosed factoring, no such intimation is provided to the debtors. However, they are told to send the payments to the new address. This type of factoring is also known as confidential factoring and non-notified factoring.
7) Full Factoring :
This type of arraignment provides the mixture of other types of factoring, arrangements. It is also called Old Line factoring and it provides various services such as credit protection and collection.
8) Invoice Factoring :
This type of factoring does not provide full service and hence is not commonly used today. The factor purchases the debts payable to the client and thus provides liquidity to the firm.
9) Export Factoring :
It is called cross border factoring or international factoring as well. Export factors provide specialized services as they have expert professionals. This type of factoring is especially helpful to the new and small scale exporters.
10) Buyer-based, Seller-based and Selective Factoring :
Under buyer-based factoring, the factor maintains a list of buyers whose receivables may be financed without recourse the seller. Under Seller-based factoring, the arrangements may be with recourse or without recourse. It is also called selective factoring as seller may not sell to the approved purchaser.
Advantages of Factoring
The main advantages of factoring are given below :
1) For Client :
The client gets following benefits from factoring arrangements:
- The client is offered liquidity as they are not required to wait till the due date of the invoice to receive cash.
- The client is able to provide better credit terms to the buyers and thus is able to generate higher revenue.
- The cash received from factoring services. may be used for ramping up production.
- The client does not require to devote time and resources for maintaining accounts.
- Factoring helps in proper management of several working capital components such as management of receivables.
- The factor is offered a comprehensive credit management system.
- The client may expand the business to new market areas.
2) For Customers (Buyers) :
Buyers receive following benefits from factoring :
- Factoring helps in making better credit. purchases as the terms are more liberal.
- Substantial money is saved through lower bank expenses.
- The customers are not required to furnish documentation. They are only required to acknowledge receiving a notification letter which contains the promise to make the due payments.
- The customers retain their rights against the seller for the quality, quantity and other such attributes of the goods and services.
3) For Banks :
These services help the banks in improving the quality of their products.
Disadvantages of Factoring
Factoring also has certain drawbacks associated with it :
1) Costly :
Such services are provided in lieu of fees and other charges, which increases the cost of carrying out the business.
2) Deleterious Effect on the Creditworthiness :
Factoring is considered to be an expensive method of financing, it is generally treated as the last resort for the firms. It has deleterious impact on the creditworthiness of the firm.
3) Credit Limits on Trade :
Various terms imposed by the factor may have negative impact on the business of the firm.
4) Difficult to Rescind the Agreement :
Due to various legalities involved, it may be difficult to come out of this type of arrangement. Changing factors involve repurchasing the sales ledger as it may have negative impact on the working capital.
5) Reliance on Factor :
The business may develop excessive dependence on the services provided by the factor.
Recommendations of Kalyansundaram Committee
Factoring services are relatively new in India. These were introduced on the recommendations of Kalyansundaram Study Group, set up by the Reserve Bank of India in 1989. Consequently, RBI introduced guidelines for factor services in 1990. SBI Factors and Commercial Ltd. (SBI FACS), the first factoring company, started operation in April, 1991. Following are the main features of factoring in India.
The committee had made following recommendations :
- India has encouraging potential for factoring services and it may be introduced by the banks as adjunct service.
- It may be offered as complimentary service to the exporters
- It is not possible to quantify the demand for such services, however, it is expected that the potential is lucrative for the sustained business development.
- It is especially useful in export sector.
- Such services may lead to dispersal of risk factors among different industries.
- The pricing of the services should be fixed based on several factors, Efforts should be made to keep the costs minimal, especially below 13.5 percent.
- The RBI may allow the factoring firms to raise funds by approaching Discount and Finance House of India Ltd. or other approved institutions. The funds may be acquired on the backing of the promissory notes.
- The financing services should be priced close to 16 percent per annum. Total price is expected not to exceed 2.5 to 3 percent of the total debt services
- Initially only qualified promoter institutions and groups will be allowed. Such groups should have solid track record behind them.
- The organizations will be allowed to work in zonal basis initially.
- Banks may have many advantages by undertaking factoring services. In the beginning. only limited number of firms promoted by such banks will be allowed to carry on the business.
- Factoring services may also be undertaken by SIDBI, in collaboration with other commercial banks.
- The bank branches should have the responsibility of educating business community about these types of services.
- Factoring services may be rendered more effectively and economically with the use of computers. It should also better communication technologies.
- The RBI should work together with the central government for starting credit investigation agencies. Such agencies may use the data collected by the banks.
- Since the businesses will avail finance from both the banks and factors, there should be proper coordination between these two agencies.
- Factoring agencies may benefit from providing these services to small scale industries.
- Such services are also beneficial to exporters. There should be uniform rules for managing such services. India may follow the guidelines provided by the Unidroit Convention on International Factoring. Banks may also collaborate with the Export Credit and Guarantee Corporation (ECGC).
- It is also important to promote competition between various players in the field. It will also provide more choices for the clients.
- For a well-organized financial system, it is important to set up appropriate legislation for regulating the business.
RBI Guidelines for Factoring
In pursuance to the recommendations extended by the Kalyansundaram Group, changes were made to the Banking Regulations Act, 1949. The RBI also issued the guidelines in July 1990 which are given below :
- Initially, the banks will not be allowed to directly or departmentally engage in factoring business. The banks will be required to use their own data for the purpose of determining creditworthiness of its clients as multiple databases are expensive to use and are also not uniform. It is also important to set up specialized credit information bureaus.
- A firm offering factoring services should not undertake financing of other businesses and factoring firms.
- Banks will not be allowed to have stake in the factoring business amounting to more than 10 percent of its paid-up capital and reserves.
Factoring in Indian Context
Factoring is a relatively new phenomenon in India. The Reserve Bank of India manages this services on regional/zonal basis. The method of using nationalized banks' subsidiaries for the purpose of providing factoring services was also preferred. It was also allowed for different banks to collaborate for offering these services. The RBI chose banks for sponsoring subsidiaries and offering factoring services on the regional and zonal basis :
- State Bank of India in the Western region
- Canara Bank in the Southern region
- Punjab National Bank in North zone
- Allahabad Bank in the Eastern zone
Only State Bank of India and Canara Bank provided sponsorship facility. Two new organizations in the private sector were set up for this purpose. Following are the four organizations offering these services:
1) SBI Factors and Commercial Services (SBI FACS) Ltd. :
State Bank of India and Small Industries Development Bank of India came together to float this organization in March 1991. The operations were started in the month of April. It is an associate member of the Factors Chain International, which is located in Amsterdam. It also as membership of EDIFACT - the communication network of the Factors Chain International for electronic data interchange for speedy communication. The firm has paid up capital of 25 crore. It accounts for 35 percent of the market in factoring segment, In turnover stood at 30 crore in 1991-92. It grew to 606 crore in 2002-03. Its outstanding purchased debt and the outstanding pre-payments stood at 156 crore and 108 crore respectively.
2) Canbank Factors Ltd. :
This was promoted by the collaboration between Andhra Bank, Canara Bank and SIDBI in August 1992. It was set up for operating in the South zone. Its paid up capital of 10 crore was offered by the participants in the ratio of 60:20:20 by Canara Bank, Andhra Bank and SIDBI respectively. RBI later removed the regional restriction on the company, allowing them to operate in the bigger market. It has augmented the paid up capital to 20 crore and had turnover of 1,223 crore at the end of March 31, 2003. The outstanding factored debt stood at 315 crore.
3) Foremost Factors Ltd. (FFL) :
It is the joint venture with the National Bank of America. It was started in 1997 and has paid up capital of 20 crore. Its current annual turnover stand at 250 crore. FFL is a member of Factor Chain International. it provides expert services in export factoring.
4) Global Trade Finance Ltd. (GTF) :
It is promoted by Export-Import Bank of India (EXIM), International Finance Corporation and West LB, Germany. It provides export factoring and forfeiting services, in addition to other services. Its paid up capital is 45 crore.
Problems of Factoring in India
Following are the main problems faced by factoring business in India :
1) Credit Information :
There is lack of resources for obtaining information. The factoring businesses are required to maintain their own databases for this purpose. Specialized agencies need to be established for this purpose.
2) Stamp Duty :
The factoring services may be liable to stamp duty. Such duties may be very high, making the cost of rendering factoring services high. Thus, it is recommended that such duties may not be charged on factoring services.
3) Legal Framework :
There is also need to change various parts of the currently legal system to smoothen the process of factoring.
4) Funding :
The factoring services are not allowed to access a wide range of funding sources which may impede their growth. their dependence on equity funding will restrict their operations. It is important to let factoring services use debt funding and money market. This will make their services more cost-effective.
5) Disclaimer Certificate :
Factors are required to obtain a disclaimer certification from banks for the purpose of purchasing the book debts of its clients. However, many banks are not willing to extend such certificates, causing problems for the factors,
6) Limited Coverage :
Currently, only domestic factoring with recourse is allowed in India. This limits the scope of operations for the factoring businesses. ECGC and SBI FACS are exploring export factoring. However, not much progress has been made in this regard. The efforts must be made to offer export factoring services to Indian exporters.