What is Master Production Schedule ?
Master production schedule (MPS) is a statement which answers certain questions like what product to be made, what number to be manufactured and timing of conducting the production process. Basically, MPS refers to production plan. Under this, the total amount of the demand of plant including the demand with regard to spares is considered. Master Production Schedule also takes into account various factors like capacity of the plant and the requirements expected from the suppliers. Certain provisions are also made in each of the manufacturing facility. MPS is responsible for meeting and planning all the material, plant, labour, tools and equipment's requirement at the plant.
Master Production Schedule is separated from production plan. As stated earlier, MPS is not basically a prediction of the sales. It rather constitutes a production plan for the manufacturing of the end product at a respective manufacturing facility. Therefore, it is limited to the production planning.
In order to ascertain the technical and the economic feasibility of the master production schedule, rough cut capacity planning is used which a medium term capacity is planning at master production planning stage. The tenure of the planning may range from 1 week to 3 months and may vary depending upon the size of the company. If demand exceeds the present capacity then some demand is postponed to the future date or some additional capacity may be added. MPS undergoes regular change as compared with the production plan. It is rather a detailed plan and is short-sighted. In a nutshell, it can also be referred to as the contract between various functional areas of a company.
Functions of Master Production Schedule
MPS has the following functions :
1) Translating Aggregate Plans :
By adopting master production schedule, various aggregating plans are made that establish balance between the market demand and the material, equipment and labour requirement of the organisation. An attempt is made to translate the aggregates into the specific units that are required to be produced with the specific time. Products are then grouped together so as to match the manufacturing facility. Therefore, one can say that MPS refers to a manufacturing plan to carry out the production
2) Evaluating Alternative Master Schedules :
The trial and error method is used for the preparation of the master scheduling. The alternative MPS are prepared and trial is made using the simulation technique in the computer. Afterwards, the requirement of the material is derived using the MPS.
3) Generating Material Requirements :
For MRP I system, MPS constitutes the basic input. MRP I system is responsible for providing the required items in respective time frame so either by purchasing or manufacturing as to meet the time schedule of the end products based on the master production schedule.
4) Generating Capacity Requirements :
When the components are manufactured within the required time frame, then that denotes the capacity requirements are duly met. MPS constitutes the base for the capacity requirement planning which includes the usage of the material and the labour. In case, the capacity requirements are found to be inadequate, master schedules are revised.
5) Facilitating Information Processing :
Master production schedule somehow manages to control the workload on the various workstations. Delivery targets for the end products, whether they are for make-to-stock or make-to-order is formulated and duly met. Other requirement of the managerial information like financial resources, marketing capabilities and the personnel policies are coordinated.
6) Maintaining Valid Priorities :
The priorities assigned to one job over the other should be real. So, accordingly, the deadline for completion of a job should match with the production line in real terms. As a result of change in orders from the customers or in case certain material is scrapped the production of the end product will be hampered as the material might face shortage. So, it becomes significant for the MPS to incorporate the modification.
7) Effectively Utilizing the Capacity :
As the end requirement is specified for a particular period. Master production schedule is able to establish the load and the parameter for the usage of the labour and the equipment's. It is further able to ascertain the requirement of any extra shifts or overtime.
Objectives of Master Production Schedule
Following are the objectives of MPS :
- To assist the top management with a mean so that it may authorize, control labour and working capital investment and the outflow of cash.
- Coordinating various managerial functions like manufacturing, marketing, financing and engineering for achieving the common target.
- For matching the needs of the manufacturing and the marketing departments.
- To get a comprehensive measure of the performance.
- To provide the base for the material and the capacity planning.
When discussing about the planning cycle, preparation of the MPS is a crucial factor. MPS brings various aspects together like material, personnel, tools and equipment's, and the facilities. Certain key delivery dates are also identified through it considering the customer requirement
Time Fences in MPS
Any changes that occur in the MPS can cause disruption, particularly when the change is at very initial stage or at a very later stage. However, minor adjustments, if any, can be made in the MPS. On the other hand, certain high performing organizations prepare the MPS in much more effective manner. To further increase the effectiveness and efficiency of the Master Production Schedule, it is made sure that time fencing is thoroughly inducted. Under the time fencing in master production schedule technique, the time horizon is split into three phases referred to as frozen, slushy and liquid. Types of time fences in MPS are explain as follows :
1) Frozen :
It denotes the phase that is expected in the very near term. Under this phase, the organisation may not be able to make the delivery of any fresh order or may have to incur huge expenditure in order to make such delivery. The vice-president of the manufacturing unit is entrusted with the job of decision-making regarding any new product. The duration of this phase extends to the total time required to manufacture the new product and the time required for procuring the materials. The delivery dates decided are most met.
2) Slushy :
This phase follows the frozen phase. Execution of the fresh orders is relatively less expensive than that in the frozen phase. Now, authority for execution of the fresh order lies with master scheduler. Just like frozen, the delivery dates decided are duly met.
3) Liquid :
The last and the farthest phase is the liquid phase. New orders and the cancellations of the existing orders can be easily made. Delivery dates given are tentative and there may be variation in the actual delivery.
In order to reap the maximum benefits of the MPS, strict following of the time fencing policies is the key. The rules are strictly followed and well communicated in the organisation.
MPS Inputs and Outputs
MPS (Master Production Schedulers) lays down the platform for building the schedule for some of the specified parent products. The scheduling function in this case is not limited to the time and the money which were the major limiting factors of the aggregate scheduling. Rather real time along with specific SKUs is considered. Sales forecast also acts as the driving force behind the master production schedule alongside actual orders in hand. Apart from this, urgency involved in certain orders and customer preference is also considered. A serious attempt is made to make the best possible use of the capacity levels and the resources available. Figure depicts the same :
Process of Master Production Schedule
Following steps are included while developing MPS. Master production schedule process steps are as follows :
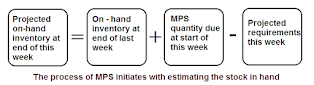
Step 1 : Estimating the Stock in Hand :
The process of MPS initiates with estimating the stock in hand. It denotes the stock that will be left after the demand is duly satisfied :
So, for the coming few weeks, any fresh MPS quantity for the product may not be required as already some balances exist. The scheduler keeps the inventory greater of the customer order or the forecasted inventory, and due consideration is also given to the fact that there can be error in the forecasted inventory. The projection made can be more accurate if the orders booked exceed the forecasts made as they denote the real quantity. On the other hand, if they exceed the orders booked for a week, the forecast will present a better estimation of the requirement for that week as some orders are yet to be booked.
Step 2 : Determine the Timing and Size of MPS Quantities :
The scheduler aims at maintaining a zero inventory level in hand by adopting the timing and the size model of the MPS. In case, any shortage is found, MPS quantities should make the relative arrangement to overcome this. But at the initial stage, the master production schedule quantity should be scheduled only for a week when any shortage is reflected. MPS quantity is added to the projected quantity in hand and the next period of shortage is ascertained. This means that there may a need for second MPS quantity requirement.
By using the chair example, the development made in the master production schedule can be easily understood. Majority aspects of the MPS are covered in this example. Table underneath depicts the breaking down of the sales and the operation plan in case of a family of chairs for a specific type of chair.
Table : MPS for a Family of Chairs
|
|
April |
May |
||||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
|
Ladder-back chair
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
300 |
|
|
|
Kitchen chair
|
|
|
|
240 |
|
|
240 |
|
|
Desk chair
|
|
400 |
400 |
|
400 |
|
|
400 |
|
Sales and operations plan for chair family
|
1340 |
1340 |
||||||
- The amount used in the MPS should be equal to the quantity that is required in the sales and the operation plan. Plans should be consistent enough in order to arrive at the economic analysis among sales and the operations plan.
- The quantity produced must be distributed efficiently over the time. Factors like historic demand of the product, promotional and the marketing affairs are also considered in deriving the specific mix. For each specific chair type, the respective lot size must be selected by the planner after considering the economic factors like the inventory holding cost and the set up cost or ordering cost.
- There must be certain capacity limitations like labour or the machine capacity, working capital, storage space that determine the time and the size of the MPS quantities. Further, considering some of the chair styles, these limitations may be acknowledged by the planner and the time and the size of production can be planned accordingly.
Figure reflects the Master Production Scheduling process. Initially, the operations are required to establish prospective MPS to ascertain that whether it corresponds to the operations and sales plans or not. Further, the Master Production Schedule is revised by the operations until a final MPS is developed that satisfies all the limitations. and is feasible enough to be implemented. At the later stage, the production plan is revised so as to match the requirements of the production and to increase the authority level wherever required. As soon as the persons in-charge accepts the established master production schedule. the operations immediately commence. Afterwards the schedule for producing the components and the assemblies can be prepared.