What is Production Planning and Control ?
The brain of a production system is the function of the production planning and its control. Under this, the aim is to make optimum utilization of men, material and the financial resources by adequate planning, controlling and coordination of production activities, that takes place to convert the raw material into the final product in the most optimum manner. It confirms that majority of the activities in a manufacturing process are planned, organised, controlled and coordinated in a proper manner for the achievement of the overall objectives.
Production planning and control constitutes the planning, scheduling, routing, dispatching and follow up of the entire production process. It further ensures that the movement of the materials, rials, productivity of the machines, and efficiency of the labour are derived in manner for the accomplishment of the common goal and the same is quantified in terms of time, quality and place. It may happen that a number of systems are in place, techniques are developed so that each one achieves its purpose. The selected system should aim at bringing economies to scale and more importantly to meet the delivery schedule.
Definition of Production Planning and Control
According to Charles A. Koepke :
"Production planning and control may be defined as the coordination of a series of functions according to a plan which will, economically utilize the plant facilities and regulate the orderly movement of goods through their entire manufacturing cycle, from the procurement of all materials to the shipping of finished goods at a predetermined rate".
According to Alford and Beatty :
"Production planning and control comprise the planning, routing. scheduling, dispatching and follow up function in the productive process, as organised that the movements f material, performance of machines and operations of labour, however sub-divided, are direct and coordinated as to quantity, quality, time and place. It is adopting as business principle the old saying plan your work and work your plan".
Objectives of Production Planning & Control
Following are the objectives of the production planning and control :
1) Nature of Input :
Manufacturing of product requires varied inputs. Quality of final product is directly proportional to the quality of the inputs that are being put into the production process. So, planning is also required to ensure that the right inputs go into the production process.
2) Quantum of Inputs :
In achieving a production level, the right mix of the inputs is quite essential. The perfect product can only be produced if the requisite mix of the inputs is taken. However, any variation in the composition will alter the final product.
3) Proper Coordination :
Proper coordination between machines, equipment's and the labour must be ensured. This will reduce the wastage's and ultimately the cost will come down.
4) Better Control :
Another name for control function is the production planning Planning is the stepping stone for the efficient control. The actual performance can be reconciled with the set standards and the deviations can be easily corrected.
5) Facilitates Uninterrupted Production :
Planning ensures that the material and the components are supplied continuously and there is no interruption. This ensures that there exist zero idle time in the production process.
6) Efficient Utilization of the Capacity :
If the capacity of the machines and the equipment's is adequately utilized, the cost of production is likely to come down.
7) Timely Delivery :
Uninterrupted production leads to timely delivery of the output, leading to minimum loss of revenue. This further builds healthy relation with the customers.
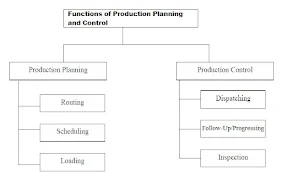
Functions of Production Planning and Control
Following are some of the role and major functions of the production planning and control :
Production Planning Functions
Following are the role/functions of the production planning :
1) Routing :
It refers to the formation of path and developing of a sequence on the basis of which the manufacturing activities will take place. This sequence is pre-decided so that the manufacturing activities can take place without hassle. Under routing, the movement path for both the materials: and the components are pre-decided through different set of machines and the work stations till the time they are converted into the finished product. It comprises of seven different activities:
- Determining what to manufacture and purchase.
- Determining the requirement of the material.
- Determining the required operations and arranging them in a sequence.
- Determining lot sizes to be manufactured.
- Determining different discarded materials.
- Determining costs associated in the production.
- Organizing different forms of production controlling.
Following are the factors that affect routing :
- Nature of the manufacturing.
- Different types of machines needed.
- Machine and different resource availability.
- Human resource factors.
According to Spriegal and Lansburgh, "Routing includes the planning of where and by when work shall be done, the determination of path that work shall follow and necessary sequence of operations, it forms a ground work. for most of the scheduling and dispatching functions of planning department".
2) Scheduling :
It refers to assigning time slots to each of the activity that is present in the sequence of the operations. It assigns the starting time and the termination time for function and ensures that the overall task is completed within the designated time. It may also be referred to as the time phase of the loading. For any operation, scheduling is the key to meet the delivery deadlines.
According to Spriegal and Lansburgh," Scheduling involves establishing the amount of work to be done and the time when each element of work will start or order of work".
3) Loading :
It means allotment of tasks to different machines depending on their capacity or load handling. It ensures that optimum load is allocated to each of the machine. After establishing the route, the next step is the allocation of the load to respective machines and the workstations. After multiplying allotted units with processing time for each of the unit, the total processing time for the machine can be calculated. This time calculated signifies the standard time within which the work is expected to be completed. This time is further added in the work that is planned for the machine. Finally, a chart is prepared representing the various jobs that a machine is handling.
Production Control Functions
The various production control functions are as follows :
1) Dispatching :
The routing and scheduling function that is discussed above forms a part of documentation only. Actual production takes. place at this stage. Dispatching takes the responsibility of transforming what is documented in a written form into the practical form following the functions of routing and scheduling.
According to James L. Landy, "The dispatching function involves the actual granting of permission to proceed according to plans already laid down. This is similar, in the case of traveler to his employer finally approving his vacation leave".
2) Expediting/Follow-Up/Progressing :
Control is said to have been exercised when actual performance follows the same path as that of the budgeted performance. In case the starting and the terminating times are duly met, there is no need to feel concerned about whether the commitments will meet the deadlines or not. The machine is said to fully utilize its capacity if it is working on the directions laid down by the plans.
3) Inspection :
It refers to the examination of a product, and verifying it for the quality control purposes and other such attributes. For controlling the product's quality, it is as important as any of the other techniques. Inspection compares the delivered results with the act standards and can occur at three distinct stages :
- Before production commences.
- During the production.
- After production terminates.
According to Alford Beatty, "Inspection is the art of applying tests, preferably by the aid of measuring appliances to observe whether a given item or product is within the specified limits of variability or not.
Phases of Production Planning & Control
Following are the various stages involved or steps in production planning and control :
Planning Phase
It includes two phases:
i) Pre-Planning :
It comprises of the demand forecasting and resource planning, product planning and its development, planning of facilities, and planning for the plant location and layout.
ii) Active Planning :
It comprises of quantity planning, routing and scheduling, product mix determination, process planning. material planning, tool planning and capacity planning.
Action Phase
The planning is now given a practical shape. It basically includes dispatching which refers to transition from the planning towards the action phase. It gives a signal to the workers to start with the production process. It includes various tasks like job order, tool order. stores issue order, inspection order, time, ticket, move order, etc.
All the reports and the orders must contain a job order number. Store issue order instruct the stores to release the material as per the requisition made and similarly, tool order instructs the tool store room to issue the requisite machinery tools as per the specifications. Time taken by different processes is embodied on the time ticket. All the gathered information is extremely useful in computing the costs of various jobs and also setting the standards. Further, all this makes the comparison quite easy and variance analysis can be made.
Job order officially authorizes the manufacturing unit to begin with the production. Normally, process sequence is tried and tested with the initial part of the production Afterwards, the same report is passed to the inspection wing through an inspection order so that quantum of re-work is reduced. Manufacturing the product requires the movement of material from the stores towards the processing workstation. A proper and efficient material handling technique is required for the same. Adequate instructions are required for moving the material and other assemblies from one place to another and that are contained in the movement order. Apart from this, those movements where the load is less, the movements can be done as per the request of the operators.
Control Phase
It comprises of two stages :
i) Progress Reporting :
Under this, data relating to the current developments made in job is gathered. It facilitates the comparison with the earlier data collected, and thus the progress made can be evaluated and analysed. The data may relate to the rejected material, equipment failure, variations in the process, efficiency of the operator, tool life, absenteeism of the operator, etc. After collecting the data, variance analysis can be done and those areas can be identified where immediate correction is required.
ii) Corrective Action :
This basically include: making provisions against the unpredicted events. It includes preparing schedule of the changes, preparing flexibility schedule, make or buy decision, modifications of the capacity, pre-planning and expediting the work, etc. A firm may encounter many unforeseen events like that of machinery break down, labour resistance, material rejection, etc., where it becomes quite difficult to meet the production and the delivery schedules. Under such circumstances, it is advisable to re-schedule product mix and also keep an alternate course of action. Expediting will be required in case the progress reporting is not up to the set benchmark. Here, the pre-planning of the complete process is must to make the expediting operations possible.
Factors Affecting Production Planning and Control
Following are the factors that affect the production planning and control :
1) Usage of Computers :
Latest automation equipment's like computers, punch cards, bio-metrics, etc., are being used by the factories nowadays. Irrespective of the volume of the operations, computers have become part of the tasks. It has facilitated the efficient management of the men and the material resources. On the other hand, some workers consider it as their competitor and fear losing jobs with the introduction of the technology.
2) Seasonal Variation :
There are certain produces where the demand is derived from particular season, as in the case of umbrella and raincoats where the demand is basically in rainy seasons. PPC tends to consider all these factors while preparing a production schedule. It may require to produce even during the non-seasonal time so that the stock can be accumulated for sale during the peak season.
3) Change in Fashion :
In the present day market this factor is of paramount importance. Thought the demand during the season can be predicted it is very difficult to predict the future fashion. If the demand of the product is fashion driven then occasional sampling survey, or test marketing is very important. Those organisations that deal in garments, cosmetics, etc., are much more influenced by this factor. A company may incur huge losses if the production is not planned keeping the preferences and the fashion in consideration.
4) Test Marketing :
Test marketing signifies that the emerging products must be test marketed aggressively to predict the future trends. This is a short duration process and many times disrupts the regular production schedule. However, PPC is required to take care of such demand.
5) Vertical Integration versus Horizontal Integration:
Mostly, the focus of the companies is on the technical areas or main product assembling. There are other small peripheral operations that are to be considered. When the sub-contracts and other sub-assemblies are conducted within the organisation, it is termed as the vertical integration and when the same is done from an outside source, it is termed as horizontal integration.
6) After Sale Service :
With the growth in the competition, this has become a key factor in the present environment. Many companies as part of providing after sale services either repair or replace the damaged articles. Both may disrupt the regular ongoing operations. However, PPC ensures to handle this extra job.
7) Loss on Account of Unpredictable Factor :
Loss may arise as a result of fire, theft or accidents in the production line to materials and the components. In number of cases, the same can be predicted. Even the shortage of material and the components may disrupt the production schedule. This may impose a real challenge to the PPC. The plans made should be flexible enough to incorporate any of such requirements.
8) Loss on Account of Predictable Factors :
Some normal losses may be there as a result of evaporation, leaking, shrinkage, shortages or other engineering flaws that are bound to occur. Such events should also be considered by PPC. However, such variations are known in advance and by using certain mathematical techniques, provisions can be made for the variations. However, it may require some extra time and resources, and thus PPC should also incorporate the same (losses).
9) Production on Order :
Sometimes, as a result of certain external pressure, there may be change in priority of few of the existing orders. However, it is up to the management to decide upon the priority level of the product. Any change will however influence the PPC. Thus, this factor also demands a consideration.
10) Design Changes :
The engineering and the R&D department may ask for some change in the design. This will again definitely require change in the input component and the process. This will further lead to change in the t pattern in which the production is carried out. It may not be possible to eliminate the change in pattern of production. but it can be reduced to a certain level. When the change is introduced after fulfillment of the current obligations, it will be an ideal scenario, In other case, adjustment is required to be made in the PPC.
11) Rejection and Replacement :
It may happen that the finished goods faces rejection at the time of conducting the final inspection. This may require certain repair. PPC should make provision to repair such defective articles without disrupting the whole production schedule.
Importance of Production Planning and Control
Following is the importance/advantages of the production planning and control :
1) Increase in Productivity :
By adopting reasonable production methods and abiding by the timing schedule, the level of productivity can be increased.
2) Removing the Hurdles :
By proper product planning and control, hurdles arising can be predicted in advance and the same can be removed.
3) Better Quality :
The quality performance in the final product is noticed by the adoption of the product planning and control techniques.
4) Consumer Satisfaction :
If the customers are provided with better quality products, then their satisfaction level is going to increase which will further enhance the brand of the company.
5) Saving in Cost :
Wastage's and possible losses can be reduced which will thereby reduce the total cost and generate the savings.
6) Increase in Production :
Uninterrupted production and supply brings smoothness in the operations. The idle time is reduced and the productivity levels are increased.
7) Optimum Utilization of Resources :
Men, material, equipment's and the financial resources are utilized in an optimum manner and there is less wastage.
8) Minimum Overtime :
Since the scheduling timelines are met, there is lesser need for the overtime and this also reduces the total cost.
9) Better Industrial Relations :
This brings harmony in the employer-employee relations which increases the morale of all the task-force.
10) Better Profitability :
With all the above points, the profits of the enterprise are likely to increase.