What is Marketing Information System ?
Marketing Information System (MkIS) is a computerized system that runs in association with other functional information systems of the organisation. The main task of MkIS is to help the management in solving problems associated with marketing of the products of the firm.
The main components of the system is equipment, people and methods that are used in collecting, scoring, analyzing, evaluating and distributing error free and timely information to marketing decisions makers. It is the task of the MkIS to understand what information the marketing manager needs. Once done it develops the framework for information collection, after that the information is distributed on time to the end users.
The main aim of marketing management is to fulfil customer satisfaction. This consists of:
- Identification of the need of the customers,
- Development of the product concept,
- Product designing.
- Product positioning in the market,
- Appropriate pricing of the product so that it can be sold in the market.
The marketing management functions are strongly related to production and financial management. This is due to the fact that marketing management is fully dependent on adequate inventory and stock, and continuous supply of goods at various locations. Marketing management controls sales in order to increase income.
There are also other responsibilities of the marketing department, such as ensuring that the market share is retained, penetration into new market and assessment of the response given by customers into the new market.
Some of the prime duties carried out by marketing management have been given below:
- Forecasting sales
- Evolving marketing strategies
- Pricing
- Designing products
- Launching products
Role of Marketing Information System
The role of a Marketing Information System is pivotal in providing valuable data and insights to support decision-making and strategic planning within an organization's marketing function. Here are key roles played by a MkIS:
- Collects data from internal and external sources.
- Organizes and stores marketing data systematically.
- Analyzes data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations.
- Provides market intelligence on trends, competitors, and regulatory changes.
- Supports decision-making by offering timely and relevant information.
- Monitors the performance of marketing activities using key metrics.
- Generates customer insights for segmentation and targeting.
- Facilitates strategic planning by identifying opportunities and threats.
- Promotes cross-functional collaboration by sharing information across departments.
- Enables continuous improvement through feedback and iterative learning.
Model of Marketing Information System
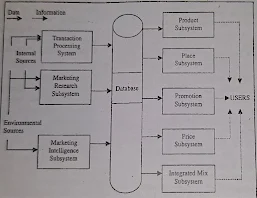
Figure shows a conceptual model of marketing information system:
Following are the various parts of MkIS:
1) Input Sab-systems:
The following subsystems ace included in this system.
i) Transaction Processing System (TPS):
This subsystem is responsible for gathering data from both external and internal sources. and the data gathered is then stored in the database.
ii) Marketing Research Sub-system:
This subsystem conduct special studies to gather external and internal data. The marketing research sub-system is used to systematically collect, analyse, and interpret information about the particular marketing subjects Whenever specific information is required this sub-system is used. Every research project has a specific time span and objective.
iii) Marketing Intelligence Sub-system:
General information regarding the development of marketing environment in the firm with the help of which the managers are able to change and develop marketing plans is known as marketing intelligence. Marketing intelligence sub-system includes the set of sources and procedures that are used to gather this information. The data. collection is usually unplanned in nature.
2) Database:
The database provides the data which is used by the output sub-systems. The data coming from the three input sub-systems (i.e., TPS, Marketing Research and Marketing Intelligence Subsystem) are stored in the database.
3) Outputs Sub-systems:
The following subsystems are included in the output sub- systems:
i) Product Sub-system:
Information about the firm's product is obtained from this sub- system.
ii) Place Sub-system:
Information about the distribution network of the firm can be obtained from this sub-system
iii) Promotion Sub-system:
Information regarding the personal selling activities and advertising of the firm can be obtained from this sub-system.
iv) Price Sub-system:
This sub-system helps the managers in planning price related decisions.
v) Integrated Mix Sub-system:
With the help of this sub-system, the managers are able to develop strategies taking into consideration the integrated effects of the various components.
Types of Marketing Information System
Here are some common types of MkIS:
1) Internal Records System: Collects and stores data on sales, inventory, and customer profiles generated within the organization.
2) Marketing Intelligence System: Gathers external data like competitor information, market trends, and consumer behavior to provide insights into the market environment.
3) Marketing Research System: Conducts primary research through surveys, interviews, and experiments to address specific marketing problems or opportunities.
4) Marketing Decision Support System (MDSS): Provides tools and data to assist marketing managers in making informed decisions, such as evaluating strategies and forecasting sales.
5) Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System: Manages customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle to enhance satisfaction and loyalty.
6) Sales Force Automation (SFA) System: Automates sales processes like lead management and order processing to improve efficiency and communication.
7) Digital Marketing Analytics Platform: Tracks online marketing activities such as website traffic and social media engagement to measure effectiveness and ROI.
8) Supply Chain Management (SCM) System: Manages the flow of goods, information, and finances across the supply chain to optimize inventory levels and meet customer demand.
Functions of Marketing Information System
A MkIS consists of the following functions:
1) Pricing of Products or Services:
Pricing of a product or a service is one of the key factors of deciding volume of the sales made. It also decides profit margin. Price determination is a very crucial as well as dynamic decision for the management as prices require to be changed frequently according to various factors like cost price, competitors' product price, demand and supply, etc. When a business competitor changes price of same type of product, the management has to take decisions like price changes etc., to remain in competition. An information system plays a very helping role in making such sensitive decisions. An Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) is widely used to get information about optimal pricing and other decisions related to marketing. There are some online product comparison engines which help customers to choose a vendor whose pricing is optimal with reference to similar products. This type of system can be used by vendors themselves to check where their products stand in the comparison.
2) Salesperson Productivity:
The productivity of salesperson varies by person to person depending on various factors such as type of product, target customer, nature of salesperson, geographical area etc. The sales data of salespersons can be collected and analysed, according to these factors, to get valuable information of productivity of them. This information can be used by a performance comparison system using factors like salesperson, product, region, time of day, etc. to create a benchmark, previous sales data can be used to compare with current sale. The benchmark metrics may be multidimensional so the analysis may require multidimensional spreadsheet software. The analysis includes salesperson, region allocated, product, price, commission, customer type, season, etc.
Online system can increase the productivity of sales force. For example, in case of a call centre, the executive while talking to old customer can view customer's purchases, demographics, region etc. and can suggest products accordingly. This information ensures prompt and better customer services. The information of customers can be maintained by Marketing Customer Information File technology (MCIF):
i) Sales Force Automation:
Sales Force automation can increase the productivity of salesperson significantly. Sales force automation provides many facilities to salespersons like access of customer history, product information, regions of service availability, information about products of competitors etc., using portable computers. A sales person can make final deal at customer's office and even book the product.
ii) Productivity Software:
There are various productivity software which can increase the performance of salespersons. Examples of such software are appointment scheduling software, document creation software, spreadsheets, EMI calculators, product catalogue viewer, email client software, etc.
3) Profitability Analysis:
Profitability analysis enables the management to know the effect of marketing efforts, price determination etc., on profit contribution of each individual product or service. The required data for the analysis is obtained from the cost-accounting system. There is various profit performance analysis software. One example of such software is Com-share (available at website comshare.com) enables the management to analyse and optimize the profit. It considers data related to nature of business, type of product, channels of distribution, geographical regions of sale etc. There is an example of Northwest Airlines, which employs expert systems and DSS to determine prices considering optimal profitability. They audit tickets and calculate commissions to travel agents, identify profitable customer using such type of software. Using this information they float special promotional offers to such customers.
4) Sales Analysis and Trends:
The data of previous sales is analysed using multiple dimensions so that previous problems as well as further opportunities can be discovered. For example, if there is a decline of certain product sale in only a specific region, then the management can focus to investigate the reason of the problem in that specific region. In the same way an increase of sale of new product can be taken as an opportunity in further decision making to launch the product in new regions.
5) New Products, Services and Market Planning:
There is always a business risk in launching a new product or making an improvement to an existing product. It involves extra cost in terms of both money and efforts besides goodwill of the organisation. There is always a question. "Will it sell?" The answer is not easy and it always requires a proper analysis, planning, and foresight. This involves multidimensional factor which require an information system and IT tools to analyse the existing data and get information for decision making. The management needs to have market foresight also due to the uncertainty in the market trends. The management also have to determine the timing when the product should be launched.
6) Market Research:
Market research is one of the crucial steps in decision making for marketing of a product or service. Market research discovers and well defines marketing problems and further opportunities by identifying consumer needs and availability of products. It discovers market segments and collects information required for decision making about launch of new products. It helps in preparing marketing strategies, evaluating effectiveness of marketing strategies and promotional activities. Marketing research also helps management in the business forecasting, financial planning, and quality control which is very vital for any new product or service to be a success.
Steps for Successful MkIS
Step 1: Potential customers are identified and segmented. Initial market research is conducted by reaching important groups like newsgroups and web servers.
Step 2: Educational material and promotional advertising are created. Multimedia effects are included in the web page. They also contain information about products and complementary products, order forms, and questionnaires.
Step 3: The materials are shown on the screen of the customer's computer. E-mail and newsgroup can be used in push-based marketing direct marketing. Web pages can be used in pull-based marketing indirect(static) marketing.
Step 4: Interaction with customers are established. Dialogues are conducted with the customer via various interactive methods regarding different characteristics of the product. Questions, answers. testimonials, and endorsements are required.
Step 5: Customers help in learning. Feedbacks that have been received from the customer are incorporated in advertising and marketing plan. New markets are identified using the experience in new product development.
Step 6: Customers are provided online service.
Applications of Marketing Information System (MkIS)
1) Accounts:
The following entities are associated with the accounting application of marketing management:
- Product sale
- Sales value
- Dealer
- Excise duty
- Inventory
- Exports market
- Product family
- Sales tax
- Customer
- Area
- Market segment
- Complaints
2) Query:
Marketing management involves the following queries:
- Product specifications
- Price and discounts
- Product quality
- Customer names & addresses
- Dealers
- Distributors
- Sales
- Stock
3) Decision Analysis:
The decisions must be taken by marketing management on the following:
- Price increase or decrease
- Allocation of stock
- Acceptance of order
- Discounts & commission
- Deciding sales terms
- Deciding new products
- Packaging of products
- Product positioning
- Distribution channels and network
The following applications are used to support such decision-making:
- Break even model
- Risk analysis model
- Distribution model
- Network model
- Product launch model
4) Control:
In order to reach the business goals, marketing management must control the following factors:
- Sales versus Budget
- Marketing cost verse Budgeted cost
- Product sale versus Target fixed for market segments
- Planned sales program versus Actual sales and sales of competitors
Inputs of MkIS
The documents mentioned below are used for feeding transactions in marketing management:
1) Customer order,
2) Order acceptance,
3) Delivery note,
4) Invoice,
5) Credit and debit note.
Outputs of MkIS
1) Product Planning:
The product planning is generally unstructured decision and complicated in nature. The success or failure of a product depends on a number of factors. The product planning decisions become more complicated due to the fact that the competitors are constantly developing and introducing new products into the market and the customer's choice are also changing. Almost all the products go through a product lifecycle. The lifecycle of a product indicates the sales of a product from its introduction stage to the withdrawn from the market. Introduction, growth, maturity, and decline are the four stages of the product lifecycle. Numerous techniques have been developed so that the manager can get the necessary information regarding the product making decisions.
2) Place Planning:
The management of distribution channels so that the product of the firm reaches to customers is known as place planning. Resources involved in the flow of the channel are supplier, manufacturer, wholesaler, retailer, and consumer. The supplier is the point from which the flow of the material originates and terminates at the customer end. The flow of money is the reverse process. However the flow of information is in both directions that connects every participant of the system.
When information flows towards the customer end, it is known as feed-forward information. Warranties, safety tips and instructions of use are some feed-forward information. When information flows in opposite direction of the flow of material, it is known as feedback information. This information includes forecasting the demand of the retailer and wholesaler, announcing new products and sales and promotion aids.
3) Promotion:
Advertising and personal selling are two principal areas of promotion. There are several reasons that make technology vital to the selling effort:
- Binding customers and suppliers
- Increased selling time
- Client site effectiveness is increased
- Detecting selling opportunities
- Increasing efficiency of sales person
4) Price:
The promotion and price area can be much close to each other based on the pricing policy of the firm regarding decision support system. There are some firms that add a desired mark-up to the cost that has been determined by following the cost-based pricing approach which is cautious in nature. Demand-based pricing is another pricing policy, which is less cautious in nature, helps the managers to establish the price depending on the value of the product as perceived by the customer. Estimating the correct demand is the key for this approach. The manager must have good knowledge about the market and the consumer including the competition and the state of the economy for this.
5) Budget Allocation:
Apart from the four Ps that have been discussed above, there are two other prime areas where decision has to be made. They are sales forecasting and marketing budget. Unlimited source of fund is never allocated to the marketing activity. The overall expenditure must be limited by a pre-determined budget. There are some computerized models that can be used to estimate mixes that are desirable in this area, but their success is limited. Personal judgement and manual means are the popular methods that make such decisions large.
6) Sales Forecast:
The marketing personnel can estimate the sale of the product in the future using sales forecast. Sales forecast is one of the major components of financial planning because it is the main source of firm's revenue. There are many technical tools that can be used to perform sales forecasting.
Reports of Marketing Information System
1) Statutory Compliance:
Duties, taxes and filing returns to the government authorities are the part of statutory compliance in marketing management. Excise duty returns, and sales tax registers and returns are the prime statutory compliance reports.
2) Knowledge Update:
The knowledge update reports in marketing management include budgets, sales, orders, stocks, and value. Some of the knowledge update reports are as follows:
- Product sales ledger
- Sales summaries
- Accounts receivables
- Received and accepted orders
- Sales analysis
- Market analysis
- Competition analysis
The format of the knowledge update reports must be presented in a summarized format and should be according to the structure of the company. Some factors that are helpful in summarizing these reports are as follows:
- Customer
- Class of customer
- Market segment
- Product
- Product family
- Sales representative
- Dealer
- Distributor
3) Operations Update:
In marketing management, the various marketing operations provided by the operations update report consists of:
- Orders received
- Orders processed
- Orders accepted
- Orders dispatched
- Orders billed
- Money recovered
This report provides details about the daily operations. Hence, operations-update reports support in preparing statistical summaries that help in getting a quick update. Below are some of the operations-update reports:
- Order book
- Dispatch report
- Inventory
- Invoice
- Customer complaints
4) Decision Analysis:
These reports help in determining whether the results realized in marketing management have been achieved or not. Market research analysis report which is a type of decision analysis report is helpful in performing sales analysis with respect to packaging, choice of market, design, price, etc. The following decision models can then be used by marketing management in association with these reports to take right decisions:
- Break even analysis
- Product market mix
- Marketing expense and market mix
5) Action Update:
Marketing management takes decisions such as allocation of more budget, product withdrawal from the market, deduction in price or changing the position of product with the help of action-update reports. Some of such reports are given below:
- Sale versus Budget
- Sales growth versus Sales objective
- Stocks versus Budgeted stock levels
- Number of complaints received versus Number of complaints serviced.
Marketing Information System Process
The process of a MkIS involves several interconnected steps to gather, analyze, and utilize marketing data effectively. Here's an outline of the typical process:
- Data Collection: Gather information from various internal and external sources relevant to marketing.
- Data Processing: Organize, clean, and integrate the collected data to prepare it for analysis.
- Data Analysis: Apply statistical and analytical techniques to extract insights and identify patterns.
- Information Generation: Interpret the analyzed data to generate actionable insights and recommendations.
- Decision Making: Use the generated information to make informed marketing decisions and formulate strategies.
- Implementation: Execute marketing initiatives and campaigns based on the decisions made.
- Feedback and Evaluation: Collect feedback and evaluate the performance of marketing activities against objectives.
- Continuous Improvement: Incorporate feedback and insights into future marketing plans for ongoing refinement and optimization.
-min.jpg)