What is Leadership ?
Leadership can be defined as the capability to inculcate confidence in employees to achieve the objectives of the organisation. It is a technique which outlines the group and organizational goals, assists in describing the groups or organizational culture and then stimulates behavior towards the realization of these goals. Effective leadership is based upon. worthy character and unselfish service of an individual towards the organisation. In order to be an effective leader, the person must possess the ability to promote changes, motivate the members of the team and lead towards the accomplishment of the common goals. It is a process of forming a surrounding where others can self-actualize, while carrying out their work. Leadership means the traits of an individual that allows him to motivate others for attaining some objectives. It is an interesting social fact that takes place in every group despite of its geography, culture, or citizenship. Effective management cannot take place without effective leadership. Leaders are the individuals, who not only foresee the changes, but also seek to persuade the employees regarding the need for change. Thus, they assist and guide the employees throughout the process of change.
Definition of Leadership
According to Hollander :
"Leadership is a process of influence between a leader and those who are followers".
According to Rosenbach and Taylor :
"Leadership is all about getting people to work together to make things happen that might not otherwise occur or prevent things from happening that would ordinarily take place".
According to George R. Terry :
"Leadership is the activity of influencing people to strive willingly for mutual objectives".
According to Chester Barnard :
"Leadership is the ability of a superior to influence. behavior of his subordinates and persuade them to follow a particular course of action".
Types of Leadership Styles
Different types of leadership styles based on authority are shown in figure :
The 3 most common leadership styles autocratic, democratic and laissez-faire are as follows :
1) Autocratic/Dictatorial Leadership Style :
Autocratic leader is also known as dictator. It could also be considered as one-man show. The role of the leader is restricted merely to dictating the instructions to his subordinates. In this leadership style, leader does not get involved with the members of the team. He decides the policies and procedures without discussing them with his subordinates and does not give any information about future strategies but simply instructs them what steps are to be taken. In this style of leadership, all decisions are taken by the leader only.
Autocratic leadership may have a negative impact because followers are unaware, insecure and afraid of leader's power. Such a leader is known as a strict autocrat who focuses on negative influences and gives instructions, which are supposed to be accepted by the subordinates These leaders are also termed as benevolent autocrat when they use motivational and positive leadership style, and some are known as manipulative autocrats, who make the subordinates feel participative towards the decision-making process even if they have already taken the decision. This type of leadership style is quite common and often gives good results. However it is subjected to the various limitations as well.
2) Democratic/Participative Leadership Style :
In this style of leadership, the authority rested with leader is decentralized. Leader takes every decision in coordination with the team members. This style of leadership is people-oriented and direct supervision of the staff is not required. This type of leadership style keeps the employees well informed about the policies of the organizations and work is delegated to achieve better results. Instead of acting as a leader, he considers himself to be a member of the group. Leader clarifies his followers that praise or blame is merely part of the group. Unlike autocratic leader, who uses his authority to control others, participative leader controls others through internal forces present within the group. The democratic leadership, another name for participative leadership style results into various positive outcomes in terms of productivity, reliability, zeal, flexibility, individual development and freedom of speech. However, the participative leader conforms that he holds to take the decision if the staff is unable to do so.
3) Free Rein or Laissez Faire Leadership Style :
Free rein or laissez faire leadership style refers to a condition where leader does not lead but leaves the major decisions on the group itself. Such a leader is represented by the chairperson who is dependent on his subordinates. All the goals are decided by the group. The group members have to solve problems and motivate themselves. Leader's job is to keep contact with outsiders and give information to his team. It can be said that free rein leadership is the inverse of autocratic leadership style.
In this scenario, the manager does not enjoy the power of control as he shares the powers also along with his work and responsibilities. It is also called permissive style of leadership as there is least interference by the leader and group works and takes decisions on its own. This type of leadership can produce wonderful results if the subordinates are highly skilled and dedicated employees. This style can be adopted successfully only when the employees are capable and competent enough to handle the situations and take corrective and positive decisions in favor of the company.
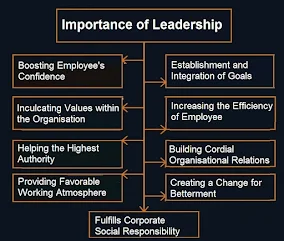
Importance of Leadership
Importance or advantages of leadership is as follows :
1) Boosting Employee's Confidence :
Good leadership is very important for the growth of the organisation as well as employees. Only a good leader can boost confidence and passion in the employees and make them work with their full potential.
2) Establishment and Integration of Goals :
It is the responsibility of a leader to establish goals for the group and integrate them with the organisation. He also provides guidance to his followers so that goals and policies can be correctly understood.
3) Inculcating Values within the Organisation :
For creating value-based organizations, it has been seen that employees of such organisation show more loyalty and faith towards the organisation and works more efficiently. It is the leader, who is responsible for incorporating such values in the organisation.
4) Increasing the Efficiency of Employee :
A good leader not only motivates the employees to perform better but he also pushes them to set a benchmark for themselves. This leads to higher productivity. which in turn leads to higher profitability.
5) Helping the Highest Authority :
Authority itself cannot bring the disciplined approach and punctuality in the team members. A good leader is required to provide the support to the authority to bring out the best talent and utilize it to maximum extent, in order to lead the organisation towards a more sustainable position in the market.
6) Building Cordial Organizational Relations :
An effective leadership is also essential to build cordial inter-personal and intra-personal relations in the organisation. It could also be used by an intelligent leader to achieve the standard goals of the organisation.
7) Providing Favorable Working Atmosphere :
Positive and conducive work environment plays an important role i improving the efficiency of the organisation. This is the responsibility of the leader to build and sustain such work environment in which employees feel comfortable, both mentally as well as physically, to give their 100% to the organisation.
8) Creating a Change for Betterment :
Generally people working in the organisation are very reluctant to change, whether it is for positive or negative. It is the duty of the team leader to inform the team members about the positive aspects of the change so that they may accept the change wholeheartedly.
9) Fulfills Corporate Social Responsibility :
An organisation which discharges its responsibility towards the society in an effective manner and maintains the work-life balance is far much reputable than other ones, which merely focus on the profit elements. It is the responsibility of a leader to maintain such a value-based system within the organisation.
Strategic Leadership
Strategic leadership is the manner of getting individuals to willingly act for the benefit of the organisation while also sustaining the short-term financial stability. Strategic leadership involves finalizing organization's strategic direction, getting the strategy in tune with the culture, incorporating great ethical principles and also making changes to the strategy of the organisation when required. Strategic leadership involves sharing the vision of the organisation with the whole organisation and getting them to act as a cohesive whole. Managerial leadership on the other hand is concerned with the day to day and short term objectives of the organisation.
It has two major facets firstly, it involves a change of the organization's size, practices, prevalent culture, values and individual so that the resultant organisation is exclusive and secondly, it lays a lot of stress on the people as the people play a big part in converting the resources of the organisation into outputs for society.
The thrust or role of strategic leadership is as follows :
- It is concerned with the vision of the organisation. The guiding principle is the mission. It is not organizational efficiency.
- It is characterized by change and it is driven by a transformational style of leadership. This is the style of leadership which recognizes the need for change in an organisation and takes action accordingly.
- It inspires people to work towards a common objective.
- In this, external focus is preferred.
Technique of Management by Objectives (MBO)
Peter F. Drucker gave the concept of MBO in the year 1954 in his seminal work "The Practice of Management". This concept envisages a management viewpoint which puts a great premium on the contributions of employees. This concept is recently being applied in the area of performance appraisal.
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a managerial approach for promoting participation of managers and employees towards the common goal fulfillment. Here, focus is on defining objectives so efficiently that both management and employees of the organisation understand their role and position and collectively work towards organizational objectives. MBO is responsible for incorporating goals and objectives of the organisation in order to improve the operational capability of the organisation. All the employees have total clarity on the objectives and get strong indications regarding the framing of their objectives, and implementation plan etc.
Through MBO each operational unit within the organisation, clearly identifies its role in attaining strategic goals. People know what is expected of them for the organisation to achieve its objectives. MBO makes a distinction between achieving an objective and getting the job done. The emphasis should be on achieving an objective. The role of the managers is to guide their assistants in the accurate direction and ensure that the right environment is created in the organisation.
Definition of Management by Objectives
According to Prof. Reddin :
"Management by Objectives (MBO) is the establishment of effectiveness areas and effectiveness standards for managerial positions and the periodic conversions of these into measurable time bound objectives linked vertically and horizontally and with future planning".
Process of Management by Objectives (MBO)
The process includes 5 steps of MBO as shown in figure :
1) Set Organizational Goal :
The first step is to set goals and objectives in the organisation. These goals may be set jointly by the superior and subordinates or they may be decided by the superiors alone. The goal is the desired outcome that the organisation wants to achieve.
2) Joint Goal Setting :
The next step is the setting of the short term objectives. This is done by means of a joint meeting between the superior and the The manager needs to keep in mind the roles and responsibilities of his subordinates. He may use an organizational chart for this purpose. The subordinate writes down his personal goals and these are then aligned to the goals that the manager has set for the subordinate. The final goals are then decided and put in writing.
3) Performance Review :
The performance standards for the decided goals are then set. These pertain for a particular time period. The subordinates thus have clarity on what is required to be done, how much has been done and how much remains.
4) Set Check Posts :
The performance is reviewed periodically to the standards set to check if the progress is commensurate with expectations. This also highlights training needs of the subordinate and also brings to the fore events which affect the organization's performance but which cannot be controlled by the subordinate.
5) Feedback :
It has been found that employees who get regular and timely feedback over their job performance are more motivated than those employees who work in a haphazard environment. It also helps the employees to know where they stand in the organisation in terms of their performance against the expectations set.