In common parlance, sustainability means the capacity to endure. In ecology, it is a term describing how biological systems remain diverse and productive over a period of time. For human beings, sustainability should be understood as the potential for long-term maintenance of well-being, which in turn rests with the well-being of the natural world and the responsible use of natural resources.
Sustainable development is defined as a pattern of socio-economic development which optimizes the economic and societal benefits available in the present, without spoiling the likely potential for similar benefits in the future. A primary goal of sustainable development is to achieve reasonable and equitably distributed level of economic well being that can be perpetuated continually for many human generations.
Sustainability in Strategic Management
From a strategic viewpoint, sustainability in corporate world is integrated with stakeholder approach and strategic management. For many scholars and business analysts, sustainability has increased in importance for organizations and is more than just "another thing to do". An investment in sustainable strategy (Sustainable Strategic Management) can reap great benefits like technological innovation and advancement, increased competitiveness and great improvements in the quality of life. The implications of strategic management depends upon the level at which a firm integrates sustainability.
For many firms, a more informal or ad hoc approach to incorporating sustainability is taken as a starting point. For example, this level might include one or two standalone sustainability initiatives that are not connected with strategic objectives of the company. The reason for these initiatives can be to improve the company's profit through increased efficiencies or as a means of demonstrating leadership and improving the company's image and reputation. However, without a more formalized approach to ensure long standing commitment, these initiatives can fade as attention is focused on other issues. In a formalized approach, the organisation releases statements regarding the understanding of sustainability and the level that it wants to achieve.
For example, Hewlett Packard in its Global Citizen For exam Report of 2010, displayed a scorecard on its various values. These included parameters like sustainability. employment norms, ethics and adherence and social innovation. The Global Citizenship report mentions specific goals and how the performance has been with respect to these goals. This is an important component of the strategy of the organisation. PepsiCo is another example of a company which mentions the following parameters and records achievement against :
- Performance - better and sustainable financial performance.
- Human sustainability - fulfilling, diverse and complex nutrition needs of the people.
- Environmental sustainability - being a good caretaker of the natural resources of the world.
- Talent sustainability - creating an environment which fosters excellent working environment and sustainable employment opportunities.
Objectives of Sustainable Development
Sustainable development has the following objectives :
- To prevent unnecessary and excessive wastage of natural resources.
- To use energy productively and make a significant improvement in the quality of human life.
- To shift the use from non-renewable to renewable sources of energy.
- To reduce the consumption of renewable energy sources to the point where they can be generated again and replenished.
- To promote fairness and equity in resource utilization.
- To initiate steps to protect the ecosystem.
- To consider environmental and economic aspects in decision-making.
- To reduce wastage in the usage o non-renewable resources and promote recycling of waste.
- To fulfill international laws and regulations related with environment.
- To mitigate waste and pollution and bring them down to levels which are bio-degradable and manageable.
- To stabilize and control rapidly exploding population.
- To reduce poverty levels that compels people to use resources in unsustainable manners.
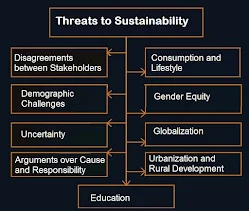
Threats to Sustainability
The various risks to sustainability are as follows :
1) Disagreements between Stakeholders :
There is a presence of many stakeholders in society, all of whom have diverse and often conflicting interests. These stakeholders belong to different segments like men, women, trade unions, farmers, employees etc. The opinion of all these stakeholders has to be considered before a decision can be taken. These opinions are often at cross purposes and hence it is often very difficult for the organisation to reach a unanimous decision.
2) Uncertainty :
The global environment is a highly uncertain and fluctuating landscape. Even the implementation of the policies becomes difficult because of environmental factors.
3) Consumption and Lifestyle :
The consumption and lifestyles of different countries need to be counter balanced. As the developing economies are seeking a better and faster growth in their standards of living, this can only be possible if the ecological footprint of the developed countries reduces, otherwise the environment will have to pay a very big price.
4) Arguments over Cause and Responsibility :
There is a lot of controversy regarding the responsibility for specific global events. A case in point is Global warming. Global warming has been caused because of the development of developed countries. However the effect of global warming is felt in low lying countries which are mostly low income and less developed. These countries now run the risk of being inundated by the sea. Sustainable development has different meanings for different classes of people. Sustainable development will not be possible unless there is complete unanimity about what it means and how it is affecting mankind as a whole, rather than individual community.
5) Demographic Challenges :
It is very important to address demographic factors for sustainable development to take place. It is very necessary to keep an eye on human parameters of development along with other measures like green economy environmental change. Demographic challenges need to be treated in a differential manner. It has been seen that developmental challenges are the greatest where there is maximum poverty and population growth, education is not developed and the susceptibility to environmental change is maximum.
6) Globalization :
The spread and advancement of technologies has also had an effect. Genetic Engineering has had tremendous effect on the environment and the health of society. Globalization runs the risk of growing festered and having a major impact on growth which will be unsustainable.
7) Gender Equity :
The role of women in many societies is still that of second class citizens. It is important that women are empowered and they occupy their rightful place in society. The worst standards of living and discrimination can be seen amongst women who are working in the informal sector, example, in the construction industry.
8) Education :
The lack of awareness on the need and importance of sustainability is often a very big limiting factor. This lack of awareness can be lessened by interjecting meaningfully at all levels of education. All the stakeholders need to be educated on the need for sustainability. It is also important that a mechanism be devised that ensures the timely transmission of knowledge from research based institutions to the market.
9) Urbanization and Rural Development :
There are also other reasons like the Government and concerned people not paying sufficient attention to the relationship between the urban development policies and the various investment strategies that are being followed with the impact on the rural economy. There is an urgent need to view all such projects and initiatives with the looking glass of sustainability and to access the various impacts that these policies are having on the rural economy.
Sustainability and Business Strategy
The formation of an does not happen by chance or by adopting an informal approach. An organisation is established with a specific objective and purpose in mind, which is the basis of a formal organisation. Corporations can also be considered as a type of formal organizations, which are created with the specific purpose of achieving defined objectives. For long, the main focus of such objectives has been centered towards the generation of monetary value.
Generally, the objectives that a company wants to achieve are expressed by its mission and vision statements. Strategy has become a method for companies to clarify their vision, perform their mission activities and realize objectives. The issue of whether the sustainability aspect of the objectives should be or needs to be a part of the company's vision is widely debated among various stakeholders.
In recent times, lot of scientific research and studies related with sustainability and business strategy (Sustainable Business Strategy) have been conducted. Such studies reveal that there can be win-win situations for companies under which they can make progress in the efficient implementation of sustainable business activities and can maximize their returns. In order to remain competitive, companies must integrate sustainable development with their business strategy. Further, the organizations need to understand the importance the relation between improved competitive advantage and incorporating sustainable development with business strategy. However, not much indication has been found suggesting that organizations will willingly move sustainability. The move will be more as result of the self-interest of the organisation or to enhance their survival chances. It is debatable as well as interesting to note the conditions that may force an organisation to take sustainability as an objective in its self-interest to achieve competitive advantage.
According to Hart's viewpoint based on natural strategy resource, companies can gain advantage over their competitors, by incorporating the sustainable development as it develops a long-term and shared vision. This theory has been very important in linking sustainability with the corporate strategy of the organisation. The long-term vision that is developed will not be a source of competitive advantage on their own but will create competencies and technologies which will further develop advantage for the organisation and improve the chances of survival in the marketplace.
By increasing their operational freedom, organisation can create financial value through its interactions with the stakeholders if the company can actively engage with the stakeholders and tell them how the company plans to fulfill its objectives while simultaneously meeting the needs of the stakeholders. The sources of competitive advantage that can force a company to incorporate sustainability in its strategy can be both internal as well as external in nature.
Applying Sustainability to Business Strategy
Even if there are incentives for organizations to incorporate sustainability in their business strategy, the logical question that arrives next is how the same. can be achieved in real life. Sustainable development strategies can be achieved by using the system conditions of sustainability and the process of back-casting (visualizing a future condition where all the sustainability norms are met and developing strategies responsible for leading the organisation to such state or condition).
According to Robert, there are four system conditions of sustainability. For a society to be sustainable, the diversity and functions of the nature are not methodically subjected to :
- Increasing output of substances which are extracted from the Earth's crust.
- Increasing consumption of such substances by society.
- Overuse and economic manipulation of the ecosystem.
- Equitable distribution and use of all natural resources for the beneficial of mankind.
The first system condition has major implication on the way fossil fuels and other resources are extracted from the Earth. It also has a critical impact on existing climatic debate and ecological side effects like carbon dioxide emissions, greenhouse gases, ozone layer depletion etc.
The second system condition relates to the efficient utilization of synthetic substances in nature especially with regards to the chemical industry. It also reflects the importance of product life cycle considerations.
The third system condition deals with the physical impact of man's actions on the ecosystem along with their functions.
The fourth system condition has major similarities with the Hart's theory which explains that sustainable development can be achieved if a balance of economic development is maintained between the developed economies in the northern hemisphere and the developing economies in the southern hemisphere.
Implementing Changes in Business Strategy
The difference between inter-organizational and intra-organizational level acts as a framework for evaluating organizational theory and management strategy. Since the intra-organizational analysis can be considered as an internal process of the company it is adopted for implementing changes in the business strategy. There are always some issues attached with the realization of management strategy due to the presence of never-ending tensions (such as division of labour, differentiation, integration, coordination) present in almost every firm. It is often difficult for organizations to get the different stakeholders like workers, supervisors, managers, etc., to work for mutual goals. This is one of the major challenges for both management practice as well as the organisation theory.
It is important to note that 95% of the personnel often do not know or understand the strategy being followed by the organisation for which they are working. This is often a case for the failure of any strategy. However, it is been shown by many management studies that implementation of a strategy and effective change can be brought in an organisation if certain key processes are followed. Doz and Kosenen have used the term "strategically agile" for organizations that are able to bring rapid changes in their business strategy and processes in response to changes in their external market.
Factors Determine Implementation of Strategy
These factors which determine the successful implementation of a strategy are as follows :
1) Top Management Commitment and Values :
The commitment of the top management has a direct as well as indirect influence on corporate environmental reactions and strategy. commitment and support that the The top management lends to a project or initiative often go a long way in making it a success.
Executives who work for "strategically agile" companies also have certain additional characteristics. Such 'new-deal executives are value-oriented and tend to be all-rounders rather being specialists. Considering on the notion of organizational learning as a basic for sustainable development, the participatory forms of leadership style and existing norms and values become the deciding factors. Thus, for implementing any change in the business strategy, the commitment and values of the top management becomes the critical factors.
2) Change Agents :
Many times, there exist individuals or groups (not necessarily from the top management) who possess the mind-set to bring about a strategic change within the organisation that will contribute in the organizational learning process. These individuals or groups are called change agents or positive deviants. The idea is to first identify those individuals and groups within the organisation who have developed successful strategies and then successfully spread knowledge about such strategies in the organisation. Change agents have been considered as one of the integral factors which have driven sustainable development organizations. In medium size organizations, change agents are often seen to exist in management positions, whereas in cases of larger organizations, they are often seen in sustainability departments or in areas like research and development.
3) Creating and Communicating a Shared Vision :
There are two critical reasons of why any effort to bring about substantial change in an organisation fails. These two reasons include lack of a strategic vision and failure to communicate and spread of vision across the organisation. The efforts made for implementing strategy which incorporates sustainable development requires significant changes from usual ways of doing business. This is why such efforts are known as transformation efforts.
The natural resource based approach of development a shared vision can also be considered as a source of competitive advantage for a company seeking strategies of sustainable development. To share a vision of the direction in which the organisation is moving and correct reason for selecting such direction are critical while implementing any strategic change.
4) Sense of Urgency :
For ensuring the acceptance of a change initiative, it is important to convince all the internal stakeholders about the urgent need for radical change. For this purpose, focus should be made upon leadership of change and significance of change efforts according to the ability of the firm to thrive and sustain. Although it has some similarities with the concept of shared vision, the urgency basically indicates that a huge and rapid change effort is required for the existence and survival of the organisation.
The usual mistake that occurs the transformational efforts is not to attach a great deal of urgency in their change management programs. As a result people do not come out of their comfort zones and no effective change can be brought about.
5) Aligning Goals on Multiple Levels :
The effect of a change process is felt across various levels of the organisation including every single person. However, it is widely observed that employees. resist any change. This is because they ignore or To bring misunderstand the positive impacts of such change on themselves and their growth. about effective change in an organisation, the personal compacts (mutual commitments and reciprocal obligations defining the relationship between employees and organizations) of people needs to be revised. It is important to bring about synergy between individual business unit objectives and the overall organizational objectives and also to align employees' personal goals, incentives and competency development plans. The friction that arises between the business, organisation and individual goals often impedes the change management process. It is therefore important that the goals across all organizational levels be aligned properly.
Integrating Social and Environmental Sustainability Issues in Strategic Management
For including the aspects of environmental, economic, and social concerns, the notion of sustainability can be widened. It is often argued that ascertaining factors is no the sustainability of environmental is not possible without considering the social and economic aspects of the related communities and their actions. For example, it is seen that building roads in wildlife regions are opposed by wildlife conservationists but this is often overcome when the benefits in the form of less congested roads and reduced traffic are seen.
Various environmental and social factors can influence the performance of companies. The likely impact however differs from company to company. Many of these factors are also dependent on each other and can thus be considered to be composite. Listed below is a portrait of various environmental and social factors important for business :
1) Water Scarcity and Quality :
Many industries are highly dependent on a source of water near their manufacturing systems. For example, food beverage industries, semiconductor companies, power plants, etc. The employees, workers and human settlements also require water for their daily needs. An increase in price of water. resource due to the increasing water scarcity will have wide ranging consequences on many industries. Moreover, the quality of available water resource is also an important factor that affects business operations.
2) Climatic Change :
There is a lot of pressure on many industries to cut emission of greenhouse gases and adapt according to the effects of climatic change because of the detrimental effect they have on the earth's ozone layer. The likely impacts on business may include affordable insurance, presence of secure energy sources and need for alternative renewable energy sources and innovations in technology. Climatic changes can also influence the logistics of raw materials. and final products. For this purpose, companies are now incorporating a shadow price (or opportunity cost) for carbon footprint in their strategic planning.
3) Energy :
The availability of energy, the cost of offering, the manner of transportation, etc., are all affected by the environmental and social factors. Due to the increasing search of alternative energy sources and costs of conventional energy resources, the issues related with environment and society offers opportunities of investments, costs reduction and technological innovation to companies as they reduce demand of energy.
4) Air Pollution :
The impact of air pollution can be seen in our daily life on human health, natural resources like forests, lakes, etc. This has led the governments to impose regulations related with the control on the amount of pollutants being emitted into the environment. Such regulations influence various business decisions like approval of new plants, operation or facility.
5) Waste and Waste Management :
The way in which companies organize and manage waste has a direct impact on the organization's profitability, product design, packaging, and production operations. There is increasing emphasis on producing more from lesser resources, which is possible if wastes are reduced and proper waste management is done. Firms can decrease their costs of production and can develop innovative concepts of waste management by investing in activities of decreasing material usage, recycling, reduced packaging and efficient waste management. It often offers opportunities of innovation and also helps firms to comply with new regulations and rules of the Government.
6) Biodiversity Loss :
The stakeholders of various industries are now paying excessive importance to the loss of diversity that occurs because of the unsustainable practices of the organizations. Biodiversity loss significantly influences the availability of resources and productivity. This is particularly true in case of industries like, fisheries, agriculture, pharmacy and beverage.
7) Forest and Soil Degradation :
Soil degradation and deforestation have affected many natural aspects such as habitats, biological diversity. quality of soil and air, etc. Consequently, this has impacted the business operations of industries like lumber and paper. The soil degradation has also affected the productivity of many crops. Sustainability practices in the area of forest and soil degradation can have a major impact on customers and the operations of numerous companies.
8) Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions :
Far away from the location-oriented impacts of people, infrastructure and ecosystems, the earthquakes and volcanic eruptions significantly influences availability of products, travel plans of personnel and management of supply chains. Although earthquakes and volcanoes are natural phenomena, their effects can be wide ranging in this age of globalization and inter-connected economies.
9) Population Growth, Urbanization and Demographics :
The rapid growth of population in developing economies is a source of cheap labour. The increase of urbanization has brought with it the demand for more energy. infrastructure and concerns about the quality of air and water. The rapid urbanization and population explosion has also influenced the availability of food demands and agricultural land, which consequently demands for improvements in agricultural practices. The growing urban incomes have driven a culture of consumerism. Under a short-term scenario, this may create different and larger markets. However the long-term, consumer. demands are supported by high-debt levels thereby influencing the sustainability of industrial growth.
10) Food Production and Safety :
The large growing population has also raised demands for greater food supply. There is a greater emphasis on safe food which is free from pollutants. Also, there is a growing demand for organic and natural sources of food. Many new industries have been born to cater this need. This growing demand for food along with features like increased safety features, degradation of climate and water, increase in energy costs, etc., have increased forest soil degradation thereby increasing the prices of food products. Further, this affects the disposable income.
11) Poverty :
The level of poverty directly impacts the demand and the pricing of many consumer products in industries like FMCG, pharmacy, telecom, etc. It also impacts the availability of healthy and educated pool of staff. Organizations that operate in poverty ridden locations often find that it is beneficial to invest in community infrastructure projects as it reduces the risks of an inadequate workforce, poor transportation facilities, etc.
12) Human Health and Safety :
There are numerous organizations that require a pool of talented and productive staff. The safety and health of the workforce is often cited as an important requirement in the sustainability of many industries. It has been also considered as an important government regulation. Thus, companies are increasingly investing in facilities for disease prevention, treatment, etc. Also, issues like AIDS, obesity, etc., are very important these days.
13) Human Rights :
Organizations and their partners like suppliers, contractors, etc., are held accountable for unfair labour practices which disregard the human rights and the laws of working conditions. This has a direct impact on the supply chains of many companies in this age of globalization. The consumers, their inter-connected communities and other important stakeholders also affect the performance of the organisation by influencing the social image of the company with the help of media tools.
14) Corruption :
Companies are also being held liable for the manner in which they conduct their business practices. Most countries in the world have enacted laws which prevent corruption and unethical practices. In the age of global supply chains, this can have a wide ranging impact on the performance of companies.
15) Social Unrest :
There are also other important issues like unemployment, riots, religious fights, political risk, terrorism, etc., that create situations of social unrest. Consequently, such situations create significant operations and business risks, including drastic threats to supply chains, infrastructure, facilities and labour relations.