What is Activity Based Costing (ABC) ?
Activity Based Costing (ABC) is a system by virtue of which the cost is allocated in different activities instead of different products and services. This further ensures that the overhead costs are assigned in a accurate manner to different products and services.
Activity based costing also ensures strategic cost management. It depicts the consumption of the resources in different activities and also allocates the costs of the products or customers on the basis of their consumption pattern. According to activity based costing, all the activities of the firm are designed to satisfy the customer's requirements. It ensures that the managers are equipped with the timely information which assists in the competitive environment and in the formulation of the strategies.
Definition of Activity Based Costing
According to Horngren :
"Activity based costing is a system that focuses on activities as fundamental cost objects and utilizes cost of these activities as building blocks or compiling the costs of other cost objects".
According to Chartered Institute of Management Accounts (CIMA), London :
"Cost attribution to cost units on the basis of benefits received from indirect activities, i.e., ordering, setting-up, assuring quality, etc." So, Activity based costing is quite general and can be adopted while using an order costing system and a process costing system.
Core Areas of Activity Based Costing
With a view to correctly attribute the costs among various products and services, ABC analysis does the same on the basis of the activities involved. The costs are allocated to the cost objects like the products and the customers based on the usage of the activities. ABC creates a network among the activity and the cost object to trace the flow of activities. There are four main areas involved in this flow :
1) Cost Object :
Just like the product and-the customer needs measurement, cost objects also require the cost measurement.
2) Activities :
They are the sum of the task involved and are concerned with the function related to the cost objects. Two types of activities exist mentioned as under:
i) Support Activities :
Support activities at e.g., schedule production, set-up machine purchase materials, inspect items, customer orders, supplier records, etc.
ii) Production Process Activities :
Under this, the production process includes the machine products and the assembled products.
On many occasions, the cost centers used traditionally and those used under the ABC system are similar. When the purchasing department and the purchasing activity, both are treated as the cost centers, the support activities will also be similar to the cost center opted under the traditional approach.
3) Cost Pool :
It may also be termed as the cost center. Thus, an activity cost center is another name for the activity cost pool.
4) Cost Drivers :
They are the reasons behind the emergence of the overhead costs. It is also a factor of change, as a result of which, change is observed in the total cost of a related object.
Steps of Activity Based Costing
Following are the steps to be taken to establish an ABC system in an organization :
1) Identifying Major Activities :
Identify the activities that share some common characteristics the sum total of tasks. For example, purchasing the material which is an activity requires different tacks like receiving a request note, inviting tenders, selection of the supplier, placing the order and receiving the material. In big organizations, the activity selected should be a major one which involves a series of tasks under it.
2) Assigning Costs to Activity Cost Centers :
Costs are allocated to the various activities which are determined above. Further, total of the amount spend on each of the activity is made. More the amount spent on a particular activity. better will be the quality of the information generated by the system. Cost drivers used under ABC system may also be known as the resource cost drivers.
3) Selecting Cost Drivers for Allocating Cost to Cost Directs :
The accumulated costs for each of the cost centers are apportioned among different cost objects. This is facilitated by the use of a separate activity cost driver. Cost driver denotes an activity that drives the costs. Cost drivers are the key events to derive the cost of the activities. These cost drivers may further be classified into three categories :
i) Transaction Drivers :
It comprises of the quantum of the orders processed, orders placed, inspections done, a number of the steps undertaken, etc. They undertake an assumption that the same quantum of resources is used at all the time when an activity is performed. So, it can be said on the basis of this assumption that the generated information is generally less accurate. In case, the resources used during different transactions are same, then the transaction cost drivers may be used.
ii) Duration Cost Drivers :
These drivers are dependent on the time required by an activity like the set-up hours, inspection hours, etc.
iii) Intensity Cost Drivers :
Under this driver, an activity is charged every time on performance. Further, direct charging is based on the actual activity costs.
4) Allocating the Cost of an Activity to Cost Objects on the Basis of Cost Driver Rates :
Rates will be calculated with the use of the selected cost drivers. Afterwards, the rates are used to find the cost identifiable with a cost object.
Cost Driver Rates = Total Cost of the Activity/Total Cost Driver Volume
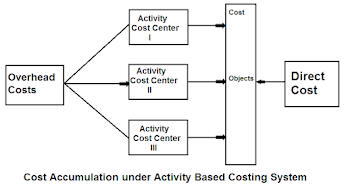
The cost accumulation process in the ABC system and the traditional costing system has been shown in the following figures :