What is Order Processing ?
Order processing is the primary factor responsible for the fulfillment of orders. It involves various activities which need to be done for catering to the final market. The operations or facilities which help in order processing are usually known the as 'distribution centers'. Usually, the term, 'order processing' defines the procedure or activities related to carrying, packing, and supplying finished goods through different modes of transportation for shipment. Several factors help in determining particular order fulfillment process or functions associated with the distribution centers.
There are distinctive needs or preferences for every distribution center, as 'same size suits everyone' principle is practically impossible for ensuring working efficiency of the distribution centers. The order of the customer acts as a stimulus that adds motion to the distribution chain. The order processing begins when an order is placed by the customer and terminates when the goods are delivered to the end user.
Definition of Order Processing
According to Johnson and Wood :
"Order processing is the phrase means how a firm handles incoming orders. More specifically, order processing is the activities that take place in the period between the time a firm receives an order and the time a warehouse is notified to ship the goods to fill that order".
Thus, it can be said that order processing refers to a number of actions for acquiring orders, keeping records, and collecting requisite items for fulfilling the order. Order cycle in its true sense is a relative term and can have different meanings as per the perspective of different persons From the perspective of a merchant, it refers to the time when order is placed by the customer till its fulfillment From the customer's perspective; it is the time when order is sent to the time, of receiving the ordered goods. The order cycle is also called replenishment cycle for commodities which are regularly needed.
Components of Customer Order Cycle / Steps of Order Processing
The buyer places an order with the distributor through a purchase document which is a legal document representing proof of deal between the two parties. All the necessary details such as item ordered, period of delivery, terms for payments, taxes incurred and other terms and conditions are included in this document.
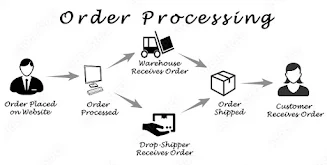
Order processing involves activities such as, order placement by customer, sending and receiving of order, checking the credit status, delivery and supply of order, order receipt, and billing. The customer order cycle is the time between order placement and receipt of the order by the customer. One of the crucial objectives of customer order cycle management involves decreasing the time taken to complete the cycle, which would ensure better customer care service and enhanced performance of logistics. The figure depicts an example of activities involved in order processing or elements of order processing :
Following are the six stages of the customer order cycle or order processing system:
Stage 1: Order Placed by Customer :
The order cycle begins with the order placement, i.e. when a customer places an order. Order placement helps in finding out that who has received the order and how, and ascertaining the techniques that have to be adopted (centralized or decentralized) for completing the order. Normally, orders are placed via salespersons, phone, email, website, or through EDI sent by central/postal address of the buyer. Nowadays, organizations prefer to receive order online, which gears up the process of product order cycle and helps in maintaining the records.
Stage 2: Order Received by Supplier :
This is the stage when orders are sent to the suppliers in batches either when the order amount has attained the pre-set amount or on a daily basis. This is done for ensuring the economies of scale. The supplier then acknowledges with the firm and begins to prepare the orders for dispatch.
Stage 3: Order Processing :
At this stage, the supplier makes arrangements of the required stocks with the help of order details. For fulfilling the customer order, the supplier may have to begin another order cycle by placing orders with its own distributors. The information about the order is also sent to the accounts department for invoicing. Order processing involves the following :
- Checking the order, if it is complete and correct.
- Checking of the credit details by the accounts department.
- Recording of transactions by the accounts department.
- Allotment of goods by inventory department and giving advice's to take the consignment and updating the records in the main inventory system.
- Shipping the order from warehouse.
Moreover, the idea of product supply chain helps in stating the desired time of receipt of order (i.e. time period within which the order must reach the customer). These types of situations demand best efforts by the supplier to deliver the order as per the customer's preference. For this purpose, rational understanding regarding the time of order placing in the line with other orders is required so that it can reach the customer without any delay.
Stage 4: Order Picked and Packed :
Picking and packing operations include delivery guidelines to a particular storehouse for collecting the customer's order. These guidelines are in written form, which convey the warehouse employees to prepare the required items according to the customer order.
Order picking and packing function involves tasks beginning from receiving the order from warehouse. to shipping it with appropriate transportation Ultimately, a list is prepared to indicate the items collected for delivery by specifying the picked commodities along-with an indication about the persons who prepared the order. This is essential for the recipient to check the list on receiving and give confirmation regarding the same. Perishable items and delicate goods should be handled with care, e.g., frozen food should be transported and stored in refrigeration.
Stage 5: Order Shipped to Customer :
On preparing the order for the delivery, it is dispatched and shipped to consumer by the distributor, organization or through outbound transportation facility. Suitable care has to be taken in selecting the transportation medium in order to keep the products intact and also for ensuring timely delivery.
Stage 6: Order Delivered to Customer :
The final step of order processing is delivery of order to the customer. The time period within which the order is picked for transportation to its delivery is known as transit time. The transit time has a major role in customers' replenishment cycle and sellers order cycle.
Thus, appropriate selection has to be made regarding planning the consignment and organizing the shipment, as any loophole might result in soaring transportation expenditure. The final stage involves sending individual orders to the customer from massive consignments. A lot of care has to be taken at this stage to deliver the right item to the right customer, simultaneously ensuring timely delivery.
Importance of Order Processing
The importance of well-organized order processing can be seen in the form of its extensive scope and intensive influence on customer care service. Advantages of order processing are as follows :
1) Attaining the Desired Level of Customer Service :
The objectives of supply chain management and logistics is to ensure the best customer care service with lowest possible expenses by optimum utilization of the available resources.
2) Establishing Relationships with Customers :
Orders act as a medium between the seller and the customer through the deal. Hence, the level of customer service can be judged through the ability of an organization to fulfill their customers orders. Usually customer relationships are linked with the number of orders delivered in right time. Good customer relationships can be established through accurate and effective order processing.
3) Developing Understanding of Customer's Need :
Order processing serves is the threshold for customers orders and queries. It helps in acquiring and fulfilling their orders through various means of communication like email, telephone, EDI, fax. website, etc. As soon as the orders are received, order processing comes into action by acquiring the required information, editing wherever needed and maintaining suitable orders. It also helps in providing the information about inventories, date of delivery, etc., and helps in fulfilling the expectations of the end users.
4) Systematic Approach to Distribution and Marketing :
Customer service and satisfaction can be attained through effective order processing. Hence, the supply chain and logistics management are mainly interested in three system outputs :
- Fast track system of order fulfillment.
- Economy in delivery of goods and services (from customer's perspective).
- Least possible wastage (through proper inventory control at different places thereby helping in optimum utilization of limited funds).
5) Retaining Customers :
Only through a well organized system of order processing, efficiency, timeliness, and preciseness in order delivery can be attained. This in turn can help in defeating the competitors and retaining existing clientele. Only timely delivery can give the organization competitive edge over its competitors.
6) Creating Repetitive Sales :
It is not a matter of luck to create sales again and again, rather it is attained by ensuring best customer service. A good customer service helps in winning the trust of customers which motivates them to purchase again and again, thus resulting in repetitive sales. Hence, fulfilling customers needs is the key to generate repeated sales and new orders.
Limitations of Order Processing
Factors affecting order processing are as follows :
1) Customer Interaction :
It refers to the time when interaction with the customer occurs. It includes the way and quality of interaction taking place. Customer interaction determines the kind of relationship an organization establishes with the customer. It reflects how much the firm is dedicated towards its customers and how much the customers are satisfied with the organizations.
2) Accuracy in Order Filling :
Preciseness in order filling refers to errors and mistakes committed while recording the orders. Though. is practically impossible to avoid all the mistakes, yet they can be controlled to a particular limit. Such errors should be minimized because a lot of time is indulged in checking, cross-checking, and refilling orders.
3) Processing Preferences :
Not all firms have abundant resources, time, and manpower for their business operations; so they have to give preference to the lucrative orders by allotting their limited assets to them. Thus, the orders. which are needed to be given preference have to be processed first and other orders are halted for some time.
4) Processing Time :
The processing time can be lowered considerably when the activities involved in order processing are cautiously organized. Performing the entire task one-by-one might extend the processing time: however, concurrent execution of several tasks might reduce the entire processing time.
5) Order Batching :
The orders which are received from many customers can be grouped together for batch processing in order to decrease the processing expenses. Conversely, the processing time for orders which entered early will substantially increase when an order is held until the desired batch size is attained.
6) Lot Sizing :
In case the customer's order is larger than the inventory size, instead of waiting for the entire order to be completed, small groups can be produced and dispatched. However, this approach might be expensive due to the additional transportation expenditure on shipping numerous small orders.
7) Shipment Consolidation :
For small-size orders, various orders can be grouped together for ensuring economy in transportation. However, it might result in increasing the processing time in an attempt to put different orders together.