What is Objectives ?
Strategic objectives are those aims that are formulated to bring major changes in response to the changes, competition, and issues in the environment. These objectives are formulated to address various internal and external issues such as target customers, target markets, product, and changes in technology, etc. Precisely, these objectives are the ultimate aim that an organisation needs needs to attain to remain competitive in the market and for its long-term survival. Strategic objectives determine the direction of the organisation in long-term and helps in allocating organizational resources.
Strategic objectives are the specified targets to be achieved in a stipulated period of time. These objectives help the managers in evaluating performances of the employees in term of quality and quantity, Strategic objectives answer the questions like-what to achieve, how much to achieve, when to achieve, how to achieve and who must achieve it.
The objectives identify the activities of the organisation. While formulating strategies, objectives help in decision-making by assisting the managers in various perspectives. The objectives also provide measures for evaluating the final performance of employees.
Definition of Objectives
According to Russell L. Ackoff :
"Objectives are states or outcomes of behavior that are desired. An organisation may desire either to obtain something that it does not currently have or to retain something it already has. Hence, objectives may be either acquisitive or retentive".
According to H. Igor Ansoff :
"Objectives are decision rules which enable management to guide and measure the firm's performance towards its purpose".
According to Robert L. Trewatha and M. Gene Newport :
"Objectives may be defined as the targets people seek to achieve over various time periods".
Setting of Objectives
In order to analyze and evaluate the performance of individuals and its impact on the organisation, the strategic objectives need to be formulated. Setting of objectives allows the organizations to establish a connection between the departments and their members, resulting into better coordination in operations and alignment of individual objectives with the common organizational goals. With no proper objective setting process in place, individual's objectives may differ from that of the organization's, which may lead to conflicts and failure.
Process of Setting Objectives
The process of setting objectives is as follows :
Step 1: Categorize the Objectives :
The first and foremost task in setting the objectives is to categorize the objectives in various categories such as long term, medium-term, short-term, etc., as per the time period of the objectives. These categorized objectives should be divided into the departmental, sectional, and individual objectives, based on the type of objectives. These objectives should be divided into a hierarchy to clarify the roles and responsibilities of people at different levels of the organisation.
After dividing the objectives, the strategic leaders need to see whether or not these objectives qualify in the criteria of good objectives. If the objectives qualify then the strategic leaders can proceed to the next step. However, if the objectives do not qualify in the criteria, then necessary modifications are done so that they can become achievable.
Step 2: Review the Areas to Cover :
Once the objectives have been divided, the next thing is to enlist the areas which need to be addressed. According to Peter Drucker, "there are eight areas in which objectives of performance and results have to be set - market standing, innovation, productivity. physical and financial resources, profitability. manager performance and development, workers performance and attitudes, and public responsibility" The strategic leaders should review the objectives and should check whether these areas are being covered or not. It should be noted, that the objectives are feasible and realistic, else the entire effort behind setting objectives will get wasted.
Step 3: Balance the Objectives:
As soon as the objectives are divided and areas are reviewed, the strategic leaders should focus on balancing the objectives. It is very essential to balance the objectives for enabling smooth operations within the organisation. It should always be kept in mind that short-term objectives should be treated as distinctive steps that lead to fulfillment of long term objectives. The objectives should be prioritized as per their urgency and significance. Hence, special attention should be paid to the short-term objectives instead of long-term objectives.
Step 4: Review the Formulated Objectives :
In the final step, the strategic leaders should review the objectives that have been formulated. The external environment is quite dynamic and changes frequently which impose certain challenges on the organisation. It is the responsibility of the strategic leaders to analyze whether the objectives meet the challenges. existing in environment. If necessary, required adjustments should be made.
Factors Influencing Setting of Objectives
There are various factors that affect the process of setting objectives. Some of the major factors are described below :
1) Environment of the Business :
Business environment and its components, i.e., external and internal environment, never remain stable for a long period of time. Changes in one or more factors lead to changes in objectives. For example, with the changes in government policies, the production policies keep changing.
2) Interests of Stakeholders :
Different group of stakeholders have different interests. Keeping in mind different interests affect the setting of objective in a significant manner. The stakeholders may pressurize the strategists to set the objectives according to their views. Since, the interests of stakeholders keep on changing with time, the priorities of objectives also change.
3) Resources and Powers of Stakeholders :
The process of setting objectives is also affected by the resources possessed by an organisation. An organisation has various resources such as human resource, financial resource, of technological resource, etc. The process objective-setting s also affected by the power of stakeholders that is used for acquiring and sharing these organizational resources.
4) Values and Beliefs of Organisation :
The values and beliefs shared by the organizational members also shape the objectives. Values mould employees' perception about making discrimination between right or wrong, good or bad, liked or disliked.
For example, if the management believes in financial rewards, then emphasis will be on financial objectives, instead of any other objective.
5) Past Trend :
Past trends of the organisation also affect the process of setting the objectives. When an organisation follows certain objectives for quite a long-time, then it becomes difficult for the organisation to leave the track. Adapting according to the changes is a gradual process, it does not occur instantly.
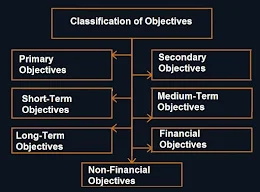
Types of Objectives
The strategic objectives can be classified following 7 types of objectives :
1) Primary Objectives :
These are called primary objectives because they are concerned with fulfilling the needs of primary stakeholders and consumers. They are the long-term goals of the organisation. The primary objectives of an organisation can be surviving in the competition, maximizing profit, increasing market share, etc. These objectives are also called as "strategic objectives".
2) Secondary Objectives :
These objectives are also called as "tactical objectives". Secondary objectives are set to perform the daily operations smoothly. These objectives address the issues of wages, compensation, incentives, recognition, etc. These are routine objectives and make a direct contribution in achievement of the primary objectives.
3) Short-Term Objectives :
These objectives are set to achieve short-term targets. The short-term goals are set for up to one year or one financial year. For an organisation, the short-term objectives can be used for increasing the sales, reducing the labour turnover, etc.
4) Medium-Term Objectives :
These objectives have longer time-period than the short-term objectives, and hence are broader in perspective. The medium-term objectives are set for the period of 18 months to five years. These objectives can be modified and reviewed whenever needed. The medium-term objectives convert into short-term objectives with the passage of time. For example, introducing variants of existing product, modification in existing organizational structure, etc.
5) Long-Term Objectives :
Long-term objectives are broad and inspiring in nature. The duration of long-term objectives is more than five years. For example, diversifying the business, acquiring or merging a new business, global expansion of business, etc.
6) Financial Objectives :
These objectives are associated with monetary benefits. These objectives are some of the core and predominant objectives of organisation. The financial objectives of an organisation can be to maximize sales, increase revenue by 20%, reducing product cost, etc. These objectives may be short-term as well as medium-term.
7) Non-Financial Objectives :
These objectives are not associated with monetary benefits. These objectives help the organisation to evaluate the intangible aspects of a business such as stability. health, long-term success, culture, value, etc. Although many of such objectives are not aligned with revenue generation, they finally have a positive impact on the financial aspects of the organisation.
Importance of Objectives
Setting of objectives is beneficial because of following reasons :
1) Provides Guidelines :
Formulating the objectives provides necessary guidelines to the employees in achieving the targets. All the activities and operations are carried-out to accomplish these objectives. Hence, formulating the objectives provide a direction to the organizational efforts. According to Wren, "Without seeing the target, a manager would be like a blindfolded archer - expending useless effort and creating havoc".
2) Legitimizes the Organisation :
Strategic objectives legitimize the organisation and allow its operations to be carried-out in the business environment. It helps in building brand image and legal status among the stakeholders and general public. This legal status leaves a lasting impression of the organisation in industry.
3) Better Coordination :
Formulating the objectives allows the organizational members to align their individual objectives with the organizational objectives. It facilitates better coordination among the employees across various departments at different levels. According to McGregor, "In setting effective goals managers help members at all levels of the organisation to understand how they can best achieve their own goals by directing their behavior towards the goals of the organisation".
4) Establishes Standards :
Objectives standards for measuring the growth of the organisation. These objectives also allow the managers to measure the performances of employees to evaluate their achievements and failures. It helps the strategic leaders to bring necessary changes when required.
5) Encourages Employees :
Strategic objectives inspire and encourage the employees at every level to improve their performances. Employees are inspired to accomplish the objectives within the time limit which contribute to the organization's success significantly.
Linking Objectives to Mission and Vision
Objectives are strongly associated with the vision and mission of the organisation. Formulation of Vision, Mission and Objectives (VMO) sets the platform for the process of strategic management The vision statements establish a basic premise, and are then defined and specified in the mission statement. The vision and mission statements lead to the formation of concrete objectives. While vision and mission statement are not specific, the objectives are achievable and specific in nature. In other words, objectives are the detailed and specified version of vision and mission statements. Usually, setting the objectives is the task of top-level management, and hence should be properly communicated to the staff at all levels of the organisation.
The vision, mission, and objectives (VMO) together perform many functions. Some of the major functions are controlling, legitimizing, coordinating motivating, etc. Strategic objectives relate the vision and mission statements and help the organisation to realize these functions. Vision statement outlines what the organisation wishes to achieve. Mission statement highlights the features and functions of the business, while the objectives set the targets achieve the defined mission and vision.
Both vision and mission statements show the way to achieve the objectives. Vision statement summarizes the objectives and mission statements sets a platforms for objectives. Hence, without setting vision and mission statements, it is nearly impossible to formulate the objectives.
Connecting the objectives with vision and mission statement is very crucial and is usually carried-out by the top-level management. The strategic plan is identified from the vision and mission statements by analyzing following factors :
- What an organisation wishes to achieve in terms of market position and market competition ?
- What are the right products and services to fulfill these aims and what is the right time to fulfill these aims ?
- What strategies should be adopted to maintain growth for long-term in this age of competition ?
The values and beliefs held by the organisation affect the objectives. While setting high-level objectives, the values should be reviewed and re-evaluated.
Difference Between Goals and Objectives
Generally, people get confused by the terms goals and objectives. Goals and objectives differ in following terms:
|
Basis
of Difference
|
Goals
|
Objectives
|
|
Meaning
|
Goals
are the idealistic situation that an organisation wishes to achieve in
future.
|
Objectives
are the managerial commitment to achieve certain desire outcomes by using
organizational resources.
|
|
Nature
|
Goes
are permanent and continuous in nature.
|
Objectives
are temporary in nature.
|
|
Time
Frame
|
Goals
are not associated with specific time frame.
|
Objectives
are associated with specific time frame.
|
|
Specificity
|
Goals
are described in general terms.
|
Objectives
are described in specific terms.
|
|
Focus
|
Goals
are generally related to external environment.
|
Objectives
are related to both the internal and internal environment of the organisation.
|
|
Measurement
|
Goals are written in abstract and relative terms.
|
Objectives
are set in specific terms.
|
Also Read :