What is New Product Development Process ?
New product development is an eight step process which involves all the key elements required for developing a product. These steps are beneficial in getting information input and decision-making while developing a new product. Other than this, market research also plays a crucial role in the process.
8 Stages of New Product Development Process
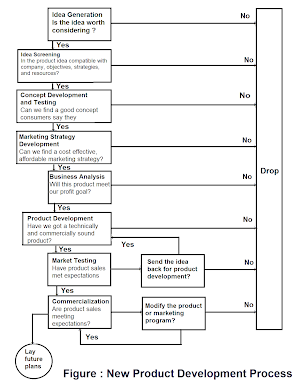
The process of new product development is shown in figure :
1) Idea Generation
The most vital and first step of new product development is gathering and evaluating new ideas to reach the potential product options. Idea generation is considered as an on-going process for many companies involving the assistance from internal and external sources of the organisation. Several market research techniques are applied to boost ideas such as running focus groups with customers, organisation's sales force and channel members, encouraging customer suggestions and complaints via website forms and toll-free telephone numbers. This can also be done by and gaining insight on product development activities of competitors through secondary data sources. Brainstorming is one of the significant research techniques used to generate ideas, where different creative thinkers collect to share their ideas and thoughts. These will help the group members to generate one idea out of another which may lead to a wide range of new products.
An idea of a new product is nothing but the product that a company can launch in the market in near future. Obviously, the competencies of the company should be in accordance with the ideas of the new product. Also, the ideas generated of such a product should be adequate in number to offer a true choice of opportunities to the consumers.
Sources of New Product Ideas
According to the various sources of ideas of a new product can be divided into the following two categories :
1) Internal Sources :
New product ideas have the below mentioned salient internal sources :
i) Research and Development Departments :
Generally, Research and Development departments are beneficial sources of new product ideas. But, only large business corporations have separate R&D departments.
ii) Technical Service Staffs :
Technical staffs are relatively more exposed to the problems of aligning the products manufactured by the company with the needs and wants of consumers. Therefore, they can be a good source of new product ideas.
iii) Company Salesmen :
Similar to the technical service staff, a salesman also understands the consumers needs, and hence exhibits an identical tendency to relate ideas, especially regarding the presentation of products.
iv) Executive Personnel :
Executives associated with the departments like research, sales, production, and administration are generally more familiar with the requirements and likely future progress of the company. Hence, they are in a good position to generate ideas that are according to the company competencies and power.
v) Company Sales Records :
Scrutinizing the sales record of the company in a detailed manner can help in determining that which product of the product portfolio is famous among the consumers, which product is failing to prove its presence, which product is in need of modification, etc. Due to such valuable information, company sales record is said to be a good source of information.
vi) Intermediaries :
Various sales intermediaries such as retailers, distributors, dealers, etc., are well versed with the consumers purchasing patterns and competitive environment, and therefore, they can be a great source of information needed for idea of new product.
vii) Top Management :
Top management personnel including directors, owners, etc., can envision new product with the help of their knowledge, expertise and experience.
viii) Company Patent Department :
Patent departments must also be recognized as important source of new product ideas. These personnel are trained and coached to comprehend in terms of new products.
2) External Sources :
There are various external sources of new product ideas, some of them are discussed below :
i) Consumers :
The lead users of the products can act as a very important source of information for the companies. The idea of famous product 'Scotch-Brite-Never Scratch Soap Pad' of 3M is a result of a customer study. The study then conducted revealed that customers wish to have such soap pads which do not scratch the utensils.
ii) Competitors :
Popular competitors (more specifically, the market leaders) can usually be considered as one of the important sources of information. From these sources, one can get the ideas like which items or variants should be made a part of the product line and which ones should be discontinued. Generally, companies want to expand their product portfolio, but the task of identifying the exact point of diminishing returns becomes very difficult. In order to determine the most appropriate product mix, the firm needs to analyse the product mix of the successful competitors. Because doing so can provide various valuable information needed for determining the product mix.
iii) Freelance Inventors :
Freelance inventors were not considered as a significant source of new product ideas, even when they have the credit of some significant product innovations on their name. Edwin Land's camera and Chester F. Carlson's copying machine are the two best examples of it. Both Chester and Edwin were rejected by many blue-chip firms and were compelled to establish their own business enterprises; today almost everyone is aware about the Xerox and Polaroid of Chester and Edwin respectively.
iv) Trade Literature :
Some companies gain information by searching several literature's. There are many examples where equipment and machinery designed and developed in different nations has later on become available and being sold in U.S. or Japan through various import channels. Therefore, by referring to the foreign literature's, a local business firm can develop identical equipment and technology, and launch it in domestic market before imports are made available in that country.
v) Other Outside Sources :
Outside sources of information comprise of trade shows, university research programmes, exhibits, consulting organisations, government research programmes, professional society meetings, etc. The major issue faced while using these sources is the technique of approaching these information sources without spending significant amount of energy and time.
Idea Generating Methods
A new idea can be generated in many ways, few of them are discussed below :
1) Focus Group :
Under the focus group technique, a discussion is held among a group of people in order to decide a new business idea. This discussion is held in an organised style. These discussions require a moderator or a leader to sit with the group of individuals, and to conduct the discussions in an explicit and open manner. Usually, focus group discussions are conducted for generating the ideas concerning the products such as cosmetics, healthcare products, apparel designs, jewellery designs, etc. This technique of generating business ideas is very efficient, practical, and less time consuming.
2) Brainstorming :
Brainstorming is also a group technique of generating new and innovative ideas and business solutions. In this method, the group members are assembled together to participate in the discussion, and to contribute their creative inputs. In brainstorming session, the knowledge. and experience of all the members are taken into consideration. The main purpose of these sessions is to canalize the ideas to a specific product or a product line.
3) Reverse Brainstorming :
It is a technique identical to the technique of brainstorming in which the discontentment and disagreement is permitted and appreciated so as to generate new ideas and solutions. Reverse brainstorming concentrates on the negative facets like "the chances of failure of certain idea","the reason which necessitates the change in product", etc. By such kind of criticism, cross-questioning, and creative thinking, new and innovative ideas are generated. The manner of criticizing the ideas and igniting discussion from it is known as Reverse Brainstorming.
4) Check List :
Discussions based on a list of related issues form the basis of developing new ideas for a business An entrepreneur tabulates a particular area of discussions and also lists out different statements, questions, and suggestions so as to conduct a thorough discussion and approach a creative business idea. There can be various kinds of questions for a specific product, few of which are listed below :
- Identify the users of the product as well as the method and purpose of using that product.
- Describe the new and different ways of using the product.
- Suggest the possible ways to improve the product in order to provide better value to consumers?
- Enlist the substitute products available in the market. Identify their competitiveness. Is it possible to integrate the features to develop a new and better product?
- Is it possible to transform the current product?, If yes then will it be a good decision?
- What changes are possible and required in the product such as packing, color, shape, size, variants, flavors, ingredients, etc.?
- Will it be feasible to introduce substitute product?
- Can the procedures and methods be changed to make them lighter and easier?
- Can customers be attracted by using good quality components, by combining units, by approaching them differently, and by introducing more positive facets?
- Identify the products which are successful in the markets of other countries. Also identify the reasons behind their popularity.
- Identify and enlist the new products that are emerging in a certain product range in the market.
5) Problem Inventory Analysis :
This technique is designed in such a way that it tries to focus on the problems for generating the new and creative ideas and solutions for the business. This method is similar to the focus group method of idea generation.
6) Synectics :
Gordon coined the concept of synectics. This technique is used to advance the process of creative problem solving. Joining together distinct and evidently unrelated elements is termed as synectics. Under this method, problems and issues are defined by "making the strange familiar" while the ideas are generated by "making the familiar strange". In other words, the purpose of this technique is to define the issue with the help of familiar terms and to distort, transpose, and invert the familiar ideas to purposely make them strange and unfamiliar. This process can invert or alter the standard expectations and standard ways of comprehending about how others will act; which in turn will give rise to new ideas.
7) Information from Publications :
A large amount of information about different products and services is available in the printed format. The printed form includes advertisements, sales brochures, publicity posters, catalogs, etc., which are easily available to every person. These publications can at times provide new ideas and business concepts.
8) Seminars and Conferences :
In order to address the emerging opportunities and challenges present in the business environment, several seminars and conferences are conducted by different institutions. Therefore, those who wish to enter or are new to business world can get a lot of useful and important tips by attending such conferences and seminars.
9) Discussion with People :
It is quite possible that if an entrepreneur is not open and attentive, he stands a chance to miss an opportunity to gain new ideas and solutions. An entrepreneur must be a good listener with an 1 open mind, i.e. he must listen and consider the ideas and inputs provided by others. These qualities can definitely help him to identify the requirements, wants, preferences and tastes of individuals working with him. And this information can be beneficial to evolve products and services that indeed possess the quality of fulfilling the needs of the customers.
10) Day Dreaming and Fantasizing :
When an entrepreneur fantasizes about a certain product or service which he wishes to have in his life, it generates a business opportunity. For example, the concept of space tourism was just a fantasy. few years back but now it is a reality. Such dreams and fantasies are responsible for inventions of many products and services.
2) Idea Screening
In this step, all the ideas generated in the first step are analysed and the best possible one is selected for new product development. Working on non-feasible ideas may be costly and risky for an organisation. Hence. the ideas generated above are evaluated effectively by the company personnel to select the most feasible idea. The screening of ideas primarily depends upon the number of ideas generated, based on which the screening process may be held in rounds like the first round comprising judgments of ideas by company executives, whereas other successive rounds may involve advanced research techniques. After the selection of few attractive ideas, a rough estimate of an idea is made, which includes its potential in terms of sales, profit, production cost. competitor's response, etc. If the ideas are suitable then they are moved to the next stage of new product development.
A new product-oriented company will at any given point of time usually have many new product deals with them. The real problem is to recognize which deal or the idea is more promising and attractive than the others. Under the new product development process, the stage of idea screening puts the different product ideas to stringent screening processes by product evaluation professionals and their committees.
An organisation is required to continuously review and reconsider its estimate of the product's overall profitability of success, as and when the new product idea moves through the development process. This can be achieved by using the formulas given below :
Overall Profitability of Success = Profitability of Technical Completion x Profitability of Commercialization given Technical Completion x Profitability of Economic Success given Commercialization
The principal basis for screening an idea can be classified under the headings enlisted below :
- Market feasibility
- Management objectives, mission, vision, policies and strategies
- Preliminary business analysis
- Legal, social, and limitations
- Technical feasibility
There are mainly two objectives on which the screening stage is based. First is to get rid of all those ideas which are evidently inappropriate of further consideration and the second is to select or shortlist from these remaining ideas which have enough potential to prove their worth.
Types of Idea Screening
A company should be aware of the following types of errors while screening the ideas :
1) DROP Error :
This error is committed when the company dismisses a good idea. For example, IBM happened to commit this error by assuming that the market for personal computer would be very small to operate for them.
2) GO Error :
This error happens when the company allows a bad idea to move through development and commercialization process which in turn causes product failures. These product failures can be of the following three kinds:
i) Relative Product Failure :
Under this scenario, the company manages to earn a profit but not as anticipated by the management.
ii) Partial Product Failure :
Here the company incurs a marginal loss as the total sales are able to cover all the variable costs and a significant part of fixed cost.
iii) Absolute Product Failure :
Here the company makes huge losses as the total sales are not even able to cover the variable costs.
3) Concept Development & Testing
Once the marketer has finalized few ideas, he initiates towards the attainment of initial feedback from the customers, its employees, and distributors. These ideas are then represented to the focus groups through storyboards, board presentations, etc.
For example, the customers may be shown the product concept by drawing the product idea on the whiteboard or an advertisement introducing the new product. They may also be presented with mock-up of ideas which may not be the actual functional version of the product idea.
The most feasible ideas selected by the organization are put forward to the target audience. What do they think about the idea? Will it be practical and feasible? Will it offer the benefit that the organization hopes? Or have they overlooked certain issues?. It is not a working prototype, but just the idea or concept that is presented to the target audience.
This is the next stage after the idea screening. Here a new product idea is put through to concept testing after undergoing the initial screening. The product concept comprises of transforming the basic idea into a particular set of characteristics and qualities the product will present to the prospective customers.
In the meantime, the 'product image' deals with the process of deciding the manner in which the product must be viewed by the consumers in the market. Also, it deals with how the product will be marketed to its potential consumers.
Once a distinct and explicit product concept is evolved, it would be expected to advance further by testing it in the market. For the purpose of testing. company can either take the sample product or the concept or both. The testing will generate feedback from the customers which will not only assist in discovering the need of any alterations or improvements in the product but it will also give certain hunts regarding whether the product will succeed in market.
Concepts Need To Be Tested and Developed
A detailed version of the idea that is conveyed in important and consequential consumer terms in termed as product concept. The concepts need to be tested and developed with a view to conceptualize and execute an idea.
1) Concept Development :
The following questions can be used to turn a product idea into several concepts :
- Who would be the users of the product?
- When the customer would use the product?
- How the customer would use the product?
- Identify the fundamental advantages that would be provided by the product.
Broadly, there are two steps involved in concept development, namely :
i) Product Concept Generation :
As per the requisites stated in product specification, a design team develops product conсере during the product generation phase. Later on these concepts are assessed and the most favorable ones are chosen for further development. The process of Product Concept Generation starts with a number of consumers needs. wants target specifications, etc. and finally ends with a number of product concept out of which the team will chose one concept as a final concept.
ii) Concept Selection :
The process of concept selection is a decision-making effort made by group of individuals Normally, concept selection stage is an important point in the entire product development process. None of the concept solutions are so clear that they team member can be aimed at because every team has his sound and valid beliefs/viewpoints on different solutions. Moreover, o company can afford wrong and ineffective decisions an they can always be damaging Proper comprehension the rules is a must for creativity and innovation Experienced judgement is necessary for the conflicting For interactions among regulatory and business model options, intellectual property, and reimbursement. Also, such conflicts occur very often.
2) Concept Evaluation or Testing :
This phase of product development process comprised of proposing the product concept to suitable target customers with a view to obtain their feedback and responses. With regards to this, a combined analysis is also done to estimate consumers inclination or interest for alternative concepts.
During concept evaluation or testing, the utility values are also derived which the consumers associate with different levels of a product's characteristics. The procedure of concept evaluation is also termed as concept testing. This process is used to estimate the success of a new product even before the stage of marketing and product launch Concept testing can be defined as a quantitative research mechanism that thoroughly determines and the the performance of completely developed conceptual probable ideas that have been developed for the purpose of fulfilling consumer wishes. Thereafter, the process advances for reducing the large reservoir of product concepts to a to a smaller and smaller number, till it reaches a viable set of concepts that can be minutely evaluated. And the final step of concept testing involves an activity wherein a representative sample of prospective customers is requested to consider the ultimately selected new product concepts, to answer some questions, and to provide certain ratings.
4) Marketing Strategy Development
After concept testing, a primary marketing strategy plan is developed. A marketing strategy is used to launch the product idea in the market. For this, a comprehensive plan laid down including the marketing mix strategy, segmentation, targeting and positioning strategy, with the expected sales and profits. The marketing plan can be categorized into three parts :
- Firstly, the marketing strategy discusses the structure, behavior and size of target market, the planned positioning of new product, estimated sales, market share and profitability goals to be achieved in the initial years.
- Secondly, the strategy outlines the distribution strategy, planned price and marketing budget for the first year.
- Lastly, the plan defines the sales and profit in the long-run and also the marketing-mix strategy for future.
5) Business Analysis
In this stage, the large numbers of ideas are condensed to one or two ideas, by the marketer During this stage, market research is used extensively to analyze the viability of product ideas. (In many situations, a product remains only an idea, if not found viable). The main aim of this step is to find out the valuable estimates of market size (i.e., total market demand), operational costs (i.e., production costs), and financial predictions (i.e., sales and profits). Moreover, it is most significant to determine if the product is suitable for company's overall mission and strategy. The market research can be directed in two ways, i.e., internal and external. Internal market research may involve discussions with production and purchasing personnel whereas, external market research comprises of customer and distributor surveys, secondary research, competitor analysis, etc. Other than all this, the organization must also scrutinize the financial viability of the product in the long-run such as cash flow generation, production cost, market share of the product and expected product life cycle.
The next step after developing the product concept and marketing strategy, the management must assess the business attractiveness of the concept. With a view to do so, the management personnel must conduct a proper calculation of total costs, sales and profits.
1) Estimating Total Sales :
It is necessary for management to determine if the sales will be high enough to earn sufficient profits. The sum total of estimated first time sales, estimated repeat sales, and estimated replacement sales is equal to total estimated sales. Purchase frequency of the product is very crucial and it acts as a deciding factor for sales estimation as well. Based on purchase frequency, products can be of three different types which are explained below :
i) One-Time Purchase Product :
The sales figures increase at the starting for such type of products; and subsequently approach zero as-most of the prospective customers are converted. The concept of one-time purchase product can be understood by considering the example of buying a home after retirement.
ii) Infrequently Purchased Product :
These types of products display replacement cycles either due to physical deterioration or eradication caused due to change in performances, styles, and attributes. Sales estimation of such products necessitates both the replacement sales as well as the first time sales. Industrial equipment, automobiles, etc. are few examples of such kind of products.
iii) Frequently Purchased Product :
For these kinds of products, the number of first-time customer increases the beginning, at decreases later on, and ultimately only few are left. As soon as the first-time buyers are served, repeat purchase orders start coming in; and finally, the sale curve fails to a plateau-like position indicating a level of constant repeat-purchase volume. Consumer non-durable items such as shampoos, detergents, bathing soaps, etc. are examples of frequently purchased products.
2) Estimating Costs and Profits :
The management must forecast expected costs and profits after drafting the sales forecast. Usually, different financial measures are used by firms to assess the benefits of a new product proposal. Out of all such financial measures, risk analysis is the most complex while the break-even analysis is the simplest of all.
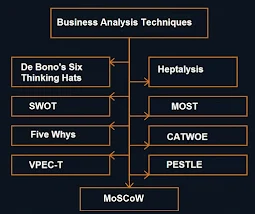
Business Analysis Techniques
A business analyst will normally make use of a series of generic business techniques while assisting the business changes. Some of the generic business techniques are discussed below :
1) PESTLE :
"PEST" or "Political, Economic. Social and Technological" analysis is one of the techniques of environment appraisal which provides a deep insight about the macro environmental factors that affect the operations of a business. The level of importance given to these factors varies as per the industry in which at company works and the goods/services it deals in. Some strategists have increased the scope of this technique by adding two more factors into it, i.e., environmental and legal factors. Hence, the extended version of this technique is known as PESTLE; it refers to :
i) Political :
Political factors are the laws. orders, and interventions made by the government in order to regulate the businesses.
ii) Economic :
Economic factors are the current and past patterns that exist in the country. These factors encompass the rate of economic growth, inflation, exchange rates, average income, etc., which heavily influence the money circulation and hence regulate the business activities.
iii) Sociological :
Social factors include all those factors that are related to the general public. These factors are closely knitted with the consumption by public such as rate of population growth, literacy rate, employment, public safety etc.
iv) Technological :
These factors involve arrival of new technology in market, automation of business processes, research and development projects, etc.
v) Legal :
It includes the effect of national and world legislation's and acts governing businesses.
vi) Environmental :
Factors related to environmental issues at the local, national, and international level come under the purview of environmental factors.
2) Heptalysis :
This technique is employed for performing a thorough analysis of businesses which are at their initial stage. The assessment is done on the basis of seven crucial categories which are as follows :
- Product/Solution
- Human capital
- Financial engine
- Market opportunity
- Execution plan
- Margin of safety
- Potential return
3) MOST :
This method is used to analyze the internal environment of an organization by elucidating the characteristics of MOST. The purpose of this analysis is to ensure the congruence of the business with each of the four features or qualities. The term MOST is nothing but the combination of initials of following four elements :
i) Mission :
The path on which the business plans to progress.
ii) Objectives :
The principal goals and targets that assist the business to accomplish, the mission.
iii) Strategies :
Decisions made for moving ahead towards the goals and objectives.
iv) Tactics :
The manner in which strategies are executed.
4) SWOT :
SWOT analysis helps the organization to design and formulate a suitable strategy that may use the available resources in an optimum way, exploit the opportunities and avoid the threats in an efficient way. The four attributes of SWOT are given below :
i) Strengths :
These are the factors that provide competitive advantage to the organization. These factors can be different for different organizations. These can be resources, skills, etc.
ii) Weaknesses :
Weaknesses are the factors that limit the growth of company or restrict the company from moving in a desired direction. A weakness can be anything such as lack of resource, lack of market understanding, lack of fund, etc.
iii) Opportunities :
An opportunity is a major favorable situation in the firm's environment. For example, loyal customers, poor substitutes, etc.
iv) Threats :
Threats are the external unfavorable conditions. They act as barrier for the organization in achieving its desired market position. Increase in tax rates, recession in economy are some of the examples.
5) CATWOE :
This technique assists the analyst in assessing about what the business is striving to accomplish. A business analyst tries to consider the influence of any intended solution on the different individuals involved. The six elements of CATWOE are explained below :
i) Customers :
Identify the beneficiaries of the highest level business process and the manner in which it exerts an impact on them.
ii) Actors :
Enlist who all are parts of the circumstance, who all will be the parts of executing solutions, and the factors which will influence their success.
iii) Transformation Process :
Which systems or processes are being influenced by the issue?
iv) World View :
Identify the broad view of the issue and also the extended consequences of it.
v) Owner :
Find out the owner of the situation or process being studied and also identify the role which they will play in the outcome.
vi) Environmental Constraints :
Identify the limitations and restrictions that will or cant influence the solution and realization of solution.
6) De Bono's Six Thinking Hats :
This business analysis technique is used specifically in a brainstorming session for producing and scrutinizing ideas and alternatives. It can be illustrative and suitable way to ask someone to go ahead and to stimulate particular types of thinking. The six thinking hats method is all about binding the group to think only in certain ways such as creating and evaluating ideas in the "mood" of the time. These specific ways of thinking are also called as the Six Thinking Hats which are mentioned below :
- Green : Emotional, Innovative
- Red : Emotional
- White : Logical, Pure facts
- Blue : Control, Cold
- Yellow : Positive, Optimistic, Bright
- Black : Devil's advocate, Negative
It is not necessary to use all colors/moods.
7) Five Whys :
The technique of Five Whys is used to thoroughly analyze what is actually going on. In this technique, every answer given is followed by a "why".
8) MoSCoW :
This method becomes useful when need of prioritizing the requirements arise. Then, the prioritization is done by assigning the requirements a suitable priority, measuring it against the credibility of the requirement, and its priority against other essentials. Prioritizing can be done by using following elements of MoSCoW :
i) Must have :
It is used for those requirements. the absence of which can cause a failure.
ii) Should have :
It is used for those requirements, which if not fulfilled, can pose a problem which in turn will need either solution or an alternative step.
iii) Could have :
It is used for those requirements, which if fulfilled, can increase the levels of delivery fulfillment.
iv) Would like :
It is used for those requirements which are needed in the upcoming period.
9) VPEC-T :
When analysis of the presumptions of many associated parties is done then the VPEC-T technique is used; provided that the parties are having different perspectives on a same system in which everyone has a mutual interest but have distinct obligations and distinct priorities. The VPEC-T is also a combination of initials of the following :
i) Values :
Values comprises of the concerns, opinions, and objectives of all the parties engaged in the analysis. They can be tangible, intangible, social, and financial.
ii) Policies :
Policies are basically the controlling tools that direct the activities, i.e., which activities to conduct and what should. be the way in which those activities can be actually performed.
iii) Events :
It comprises of real-world proceedings due to which activities take place.
iv) Content :
Content includes that significant part of messages, documents, and discussions, which are developed and used by every facet of the business.
v) Trust :
It is an essential element which must be present among the parties involved, so that they can access the information of each other and exchange it with their mutual consent.
Factors to be Considered in Business Analysis
Following factors should essentially be considered during a business analysis :
1) Product's Relationship to the Existing Product Line:
In majority of the situations, it is considered feasible to add only those new items or product lines to the portfolio which are either by any means associated with or are compatible with the current product mix. Yet, some companies deliberately include such products to their product mix which are quite different from that of the existing ones. For example, suppose a new product is launched by a company due to any of the possible reason. Now if the product is entirely new in the product line then it must, to a certain extent, has a family relation with the current products. Or else, this new product will necessitate expensive modifications in the production techniques, promotion strategies, distribution channels, and other sales strategies.
2) Cost of Development and Introduction :
The process of developing. launching, and commercializing the new products is quite expensive. This is one of the main problems of adding new products to the portfolio by the firm. Substantial capital expenditures such as marketing research to establish sales potential. expenses incurred for design and development, additional machinery and equipment, patents and necessary certifications, advertising, sales: promotion, etc., are very essential. It is also seen that a new product generally starts generating profit for the company at least after one to three years of its inception.
3) Available Personnel and Facilities :
It is always beneficial to have sufficient skilled labour as well as effective machinery and equipment. instead of recruiting more employees and buying extra equipment. Hence, it is generally more appropriate for the firm to launch new products if they already have the necessary equipment and skilled personnel.
4) Competition and Market Acceptance :
The final but one of the most important factor to be considered in a business analysis before planning to launch a new product is to evaluate the probable competition for the new product in the target market. If it is found that the competition for planned product is sever then it is advisable to drop the idea. According to several studies, a new product can be initiated in the market successfully only if it can secure at least 5% of the total market easily. Therefore, the perfect solution would be to introduce a product that is either well distinct from other existing products or it should be placed in a price bracket where it can prevent direct competition with existing players in the market.
6) Product Development
A prototype of the product is produced at this stage. Before launching the prototype in the market, it must clear all the tests and then finally the product is offered to the target audience. While doing business analysis, the suggestions and ideas are given due consideration. The initial design or prototype of that idea is then developed by the research and development team. The marketer also designs a marketing plan for the idea, and once the prototype is ready, it s introduced to the customers
Unlike the concept-testing stage, in this stage the customers go through the actual product or idea and its related such as marketing mix, distribution channels, etc. On the basis of customer reactions about the product, marketer is able to take decisions for the final market launch while, considering the purchase rates and customers' needs and wants. The prepared prototypes are tested through particular tests like functional as well as consumer tests. These are described below :
1) Functional Test :
In order to test the functional aspect of the prototype two types of tests are used by organization's, i.e., Alpha testing and Beta testing:
i) Alpha Testing :
Firstly, a particular prototype is tested within the organization with respect to different applications so as to determine its performance. It is called "Alpha testing. After implementing the necessary inputs in the prototype it is exposed for beta testing.
ii) Beta Testing :
Here, the organization involves a particular set of customers who are asked to use the prototype and accordingly give their feedback to the firm regarding their experiences while using the prototype. According to Tom Peters, Beta test is very beneficial in the following cases :
- When complete knowledge regarding the possible applications is not known.
- When opinion leaders are required from early adopters.
- Where the prospective customers are of heterogeneous nature.
- When several decision makers are involved in taking the buying decision regarding the product.
2) Consumer Test :
It involves testing the prototype as per the benchmark of the customers. In this customers are allowed to test the prototype through different methods. They can be invited in the labs of the organization to directly test the prototype or samples may be provided to them to be used in home. There are plenty of techniques to determine the preferences of the customers, which are as follows :
i) Rank-Order Method :
Here the consumer is asked to rank the products in order of their preferences or liking's such as A>B>C.
ii) Paired-Comparison Method :
It illustrates the pair of items, and request: the consumers to select one preferred item from each pair such as preferring A to B or B to C.
iii) Monadic-Rating Method :
In this method, the customers are asked to rate their liking for each product on a specified scale such as A-4, B-7 and so on.
7) Market Testing/Test Marketing
The word 'test' refers to examination or trial. Test marketing is defined as the process of testing a product before it is commercialized in the market at large scale. Here, test marketing is also known as t field-testing. This provides a better understanding of the market and marketing considerations like nature of demand, competition level and consumers needs and wants. Test marketing of a product is done within a particular market area so as to monitor the marketing mix strategy and if required, it is revised before launching it nationally.
According to Philip Kotler, "Test marketing is the stage at which the product and marketing programs are introduced into more realistic market settings".
The prototypes or products which have made it to the product development phase are now to be tested in real market. It is called 'market testing' or 'test marketing'. It is crucial to have inputs from large group of customers so as to make the product acceptable at commercial level. But, market testing is avoided by some marketers as they improve their products as per the concept testing phase and do not want to waste their effort on market testing. The commonly used market testing method is one in which the product is made available to a small segment of the target market (e.g., a city), wherein all the marketing efforts are being applied similar to any other existing product the customers could purchase.
Reasons For Undertaking Test Marketing
The two main reasons for undertaking test marketing are as follows :
1) To Know the Reactions of the Consumers :
The foremost reason for undertaking test marketing is to understand the reactions of the consumers and to anticipate or estimate the sales when the product is commercially launched in the market. on a large scale.
2) To Know Alternatives :
The marketer gets a chance to know the real reason of the product not being accepted by the customers. Test marketing also gives one more opportunity to the marketer to identify the areas of improvements that needs to be implemented to make the product more acceptable and famous among the customers.
A "post-test market launch survey" is required to be conducted by the company to make test marketing more effective and rewarding. Through this survey, the organization can determine whether the consumers are liking the product and buying it. whether the advertisement efforts are fruitful and whether the customers are satisfied with the product.
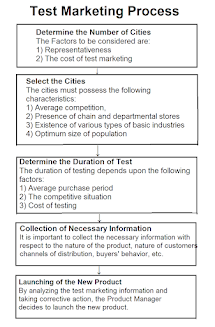
Thus, the marketing mix of the product is modified as per the findings of the survey so as to make it appropriate for the final launch. Figure shows a classic test marketing process.
Types of Market Testing
Two major types of market testing are as follows :
1) Consumer Goods Market Testing :
Four major variables namely trial, first repeat, adoption and purchase frequency are evaluated by the organizations for market testing of consumer goods. The four important consumer goods market testing methods in ascending order of expense (i.e., from least expensive to most expensive) are as follows :
i) Sales Wave Research :
In this, the consumers who were initially offered the new product free of cost are re-offered the product at a lower price. Certain competitive products may also be offered to such customers at lowered prices.
ii) Simulated Test Marketing :
Under this method, feedback of the customers is taken regarding brand familiarity and preferences in case of particular product category.
iii) Controlled Test Marketing :
In controlled test marketing, the new product is introduced in few stores by paying some fee to the stores for managing the products.
iv) Test Markets :
Using test markets, is the crucial technique of consumer product testing. In this, the new product is introduced in few major cities with the intention to capture the shelf space in every store. Organization's use their sales force vigorously to improve the sales of the product.
2) Business-Goods Market Testing :
Generally, functional tests are used for business goods and technologies. Both alpha and beta tests are implemented so as to gather the required information. In alpha tests, the business good is tested within the organization so as to measure its performance with respect to different applications. Whereas, in beta tests, few external customers are asked to use the product and give their feedback.
After alpha and beta testing, the information, gathered is conveyed to the technical team for reviewing it. With the help of such information. the technical team find outs the probable shortcomings and defects in the product. An appropriate executive committee generally conducts an assessment during this phase of product development. The committee also gives directions with regard to the future orientation of the project. These recommendations are formed on the basis of research conducted in the former stages along with appropriate economic and marketing information available to them. There can be further research in case the gathered information seems be insufficient to inappropriate. In case of severe issues or defects, further technical developments can be allowed or in worst conditions the project can be cancelled.
Importance of Test Marketing
Following points reflect the importance of market testing :
1) Product Evaluation :
Market testing is a method which enables a marketer to evaluate a new product in the real environment so as to predict its sales.
2) Evaluation of Alternative Marketing Strategies :
Different alternative marketing tactics can be assessed by the marketers with the help of market testing as it encompasses developing database of potential customers and their buying behaviors.
3) Setting of Competitive Structure :
The overall marketing strategy, i.e., pricing, distribution, promotion, etc., is evaluated by marketers in market testing so as to determine the current demand patterns and competitive environment.
4) Highlighting Scope of New Product :
It helps to obtain basic or preliminary information required for making the best possible marketing decision. It also reveals the information such as benefits and drawbacks of particular product, required changes for modifying and improving the product, new applications and uses of the product, etc.
5) Sales Forecasting :
Market testing also helps to evaluate the future sales of the new product. Moreover, the firm can prepare itself to produce the required quantity of product to fulfill the future sales needs through installing required production capacity.
6) Identification and Removal of Defects :
Through market testing, marketing related issues such defective pricing, inappropriate as distribution channels, ineffective promotion methods, etc., can be identified and reasonable solutions can be developed so as to make the product acceptable at large scale.
7) Formulation of Policy Concerning Middlemen :
Through market testing, behaviors and responses of middlemen can be determined. It ultimately leads to the formulation of policy concerning the middlemen. This policy assists the middlemen to show their best sales promotion efforts.
8) Determination of Consumer Responses :
In market testing, behaviors and responses of customers concerning the new product as well as the competitors' product can be determined.
8) Commercialization
Commercialization or launch is the final step in any new product development process. As soon as the product is market tested it becomes critical to launch the product in the target market. The overall success of a new product greatly depends upon its effective launching. The process of launching a product is definitely something more than just following a simple checklist. It's a result of well-planned and dedicated work of a well-coordinated and focused team. Every group member contributes towards planning each and every step and combining all of them 1 to launch the product successfully. Sometimes, in presence of poor strategic approach, conflicts over roles and responsibilities other critical organizational issues, certain promising products get failed. All the necessary steps namely, appropriate volume production, generating essential documents, preparation to install and support the product, managing distribution channels, planning and applying marketing activities and training sales and support personnel (both inside and outside the firm) should be undertaken during the product launch process.
Once the product passes the test marketing stage, then the product goes for national launch. However, few factors are considered before finally launching the product in the market such as time and place of launching, whether it will be launched nationally or regionally, how it will be launched, etc. Some of the organizations prefer introducing the new products region by region. This helps the organization to manage its production activities in an effective manner and also improvise the marketing mix while, approaching a new region.
Few organizations launch or introduce the new product in waves. Under this scheme, a certain portion of the market receives the product on one schedule, while other segments receive it on other schedules respectively. This enables the firm to develop a controlled production capacity and to make required changes in the marketing mix as the product is distributed to new areas of the target market. Commercialization process involves huge expenses of the organization.
Decision to be taken to commercialization
There are certain decisions related to commercialization which are very important and need to be taken accurately and rationally. These decisions are as follows :
1) When (Timing) :
The timing of entry of the product in the market is very crucial. The company introducing the product has three following options regarding when to launch the product :
i) First Entry :
In first entry, the product becomes the first of its kind to enter the particular market. As the the available distributors and customers are covered through the new product and leadership, and reputation is developed in the market, 'first mover advantage' is enjoyed by the product. Sometimes, it becomes harmful for the products to be first in the market (faulty image) without testing it thoroughly.
ii) Parallel Entry:
Parallel entry means a firm can plan the entry of its product simultaneously with the competitor's product entry.
iii) Late Entry:
In this, the entry of the new product is kept delayed so as to deal with competitors products. This move has certain advantages :
- Cost of educating customers is borne by the competitor,
- The potential faults or shortcomings can be identified by observing the competitors' product,
- Useful in learning the size of the target market and profitability of the target market segment
2) Where (Geographic Strategy) :
The firm has to decide upon the geographic strategy for the new product, i.e., to plan if the product will be launched in only one area or region or in different areas or regions, or in national or international market.
3) To Whom (Target-Market Prospects) :
The most promising target market should be focused. with effective distribution and promotion efforts.
4) How (Introductory Market Strategy) :
An action plan needs to be devised by the marketers for launching the new product into the roll-out markets.
Phases of Commercialization/Product Launch
When all the above steps in the new product development give a positive response, then launch of new product is undertaken. Following are the four phases involved in the product launch process :
Phase 1: Pre-Launch :
Developing skilled sales force. as well as marketing team is the foremost step of the product launch cycle. This stage is comprised of various activities including establishing service locations or facilities, building machinery and equipment, hiring a promotion agency, etc.
Promotional methods and press releases should be used by marketers to publicize the launch of the product. Distribution related decisions are also crucial at this stage. A reliable storage location should be identified for the stock and locality of distribution centers or retailers should also be determined.
Phase 2: Announcement :
This is the second phase of the commercialization stage which involves display or public view of the new product through press conferences, trade shows or road shows. Such announcement can also be seen as a part of firm's expansion plan. Hence, the firm may determine that which particular platform it plans to use launching its product. for For example, Tata Consultancy Services conducted several trade shows and road shows to increase awareness among the public regarding the launch of its new generation personal finance management software named as EX Personal Investment Manager which was primarily at the retail segment.
Phase 3: Beachhead :
Convincing the customers to try the product in the first instance and then inducing its re-purchase, is the prime intention of beachhead. This phase focuses on repeating as well as strengthening the original announcement. It is the t beachhead phase in which all the refinements or alterations related to the product's services, distribution, packaging, etc., are performed. With the increase of the sale of the new product this phase ends.
Phase 4: Early Growth :
Early growth phase of commercialization is characterized by repeat purchases by the target customers. Purchasing firm's product becomes a routine behavior of the customer's Due to increasing popularity of the new product of the firm, the competitors get active and start working on their respective products. They start designing new uses for their products or develop new products by imitating the firm's product. Thus, it becomes very challenging for the marketers to maintain their position in the market in terms of product price, quality, distribution, promotion, etc.
Methods of Commercialization
A new product can be introduced in the target market with the help of these to general methods namely :
1) Immediate National Launch :
This method is beneficial in two ways, firstly, it helps to prevail over competition and secondly, it saves the expenses incurred on the cost of launch. However, the risk associated with this method is that it causes several problems to the firm which could not have been recognized during the test marketing step. Production standards that function in a satisfactory manner theoretically may not always result as the same practically. During the actual launch of the product, supply: of product may act as a hindrance.
2) Rolling Launch :
The firm can choose this method as an option against full national launch. This technique includes the process of shifting towards complete national coverage by initiating the launch process with few well-known distribution areas and then later on slowly including new areas having experience to enhance the chances of success of the launched product. Rolling launch is also beneficial to the firm in managing logistics and production schedules, and keeping it in tune with the market demand. For example, many well-known brands namely, HLL, Kellogg's, Coca-Cola and several others use the strategy of rolling launch.
Factors to be Considered in Commercialization
Various factors to be considered in commercialization are as follow :
1) Launch Timing :
The first and foremost factor to be considered in commercialization is the launch timing, i.e., launching the product at right time. This means that the marketer should keep in mind both correct timing to launch in market as well as the time during which competitor's products is being launched. It may happen that a firm may plan to launch its product at the same time as its competitor in the market. Therefore, at this time, the firm may plan to :
- Launch the product before competitor to enjoy the benefit of first mover.
- Launch as a late entry so as to understand the situation of the market on the basis of the responses from customers,
- Launch the product at the same time as that of the competitor, i.e., a parallel launch.
Launch timing can be classified into following types based on timing of the product, its service launch, customer's point of view etc.
i) Premature Launch :
A premature launch is defined as a launch when the supporting system or infrastructure is not available and still the firm plans to launch the product.
ii) Right-Timed Launch :
The perfect time at which the need of the product is felt by the market or the advantage it is going to deliver is perceived by the market is termed as right time launch. Examples of right-time launches can be Jan Shatabdi Express trains, prepaid cards, free SMS etc.
iii) Outdated Launch :
This type of launch happens when the requirement of the customers is fulfilled by other sources or where the product is launched much later than the competitors or when the technology being offered by the product or service is outdated. Examples of outdated launches can be tooth-powders, pagers, typewriters etc.
2) Coverage of Launch :
A product can be launched at the local, regional, multi-regional national or international levels. Large business organizations having a well-established distribution network and sound financial are the only ones who are capable of launching at national or international Due to several power risks associated with international launches, only few big firms are able to plan the launch at international level. Process of phased roll-out needs to be followed by the firms in order to remove the risks involved in coverage of launch.
3) Phased Launches :
As the name suggests, in phased launches, companies launch their products in a finite market area before entering. the entire national market. Many companies followed this trend while introducing their new products in India including Motorola, Coca-Cola, etc. Famous brand Lipton launched its product Lipton Ice Tea by following the phase launch technique; it initially launched the product in Southern India and then slowly expanded throughout North India.
4) Target Markets :
One of the most important factors to be considered during the product launch is target market. Usually, a firm targets the best possible group of the roll-out market discovered even within the roll-out strategy. A roll-out market is the one where new product is released in support of wide promotional and advertising activities. This first set of market and customers which the firm is targeting for promoting, selling the product and providing other related services termed as prime prospects. The main motive behind conducting such exercise is to generate large sales figures as quickly as possible in order to attract more customers.
5) Buying Cycle :
The amount of time taken by customers to make a re-purchase order is termed as the buying cycle. This buying cycle differs from one product category to another. For example, in case of Fast Moving Consume Goods (FMCG) the buying cycle ranges from 10 to 27th day of a month. For this reason, the most preferable time for launch of FMCG good is the starting of the month. Similarly, the firm which are part of the white goods sector may decide to launch their product from the month of September to January i.e. during the festive season of India.