What is Object Oriented System ?
Object oriented systems represent data as objects. Other objects and users interact with these objects. Both the data and the information related to the executable file required for the data interpretation are comprised of object.
In case of object oriented system users focuses on the tasks not on the tools. The collaboration among the objects determines the behavior of the system. Collaboration is carried out by exchanging messages among the objects. Message sending is not similar to the function calling, as in this case the decision regarding what function is executed for servicing the message lies totally with the object.
A number of functions might execute a particular message. This election will be done based on the state of the object under consideration. Depending on the location of the objects taking part in the communication and the architecture of the system different types of message sending implementations are done.
Characteristics of Object Oriented Programming
The Object-oriented paradigm (OOPs) has many features like :
1) Objects :
Objects represent entities of the real world and are invoked at the runtime. They consist of data (properties) and operations (functions) to work on these data. The actual object created at the runtime is known as instance. According to programming jargon it is said that the Lassie object is an instance of the Dog class. The state of an object is defined by the set of values of the attributes. Behavior and state that is defined in the class of the object together construct the object.
2) Instance :
Class instances are known as objects. The communication between the objects is considered in order to analyse a programming problem. At the time of execution interaction between the objects are done by exchanging of messages. The objects do not know the details regarding the code or data of the objects in order to carry out interaction with each other.
3) Classes :
A new kind of static or compile time definition is class. It is a collection of data and the related functions or operations. From these classes, instances can be created at the runtime. A class is made up of objects of the same type. One can create multiple objects of a class once it has been created.
Class specifies the abstract properties of the objects along with their features which contain attributes, fields or properties. The operations or methods performed by the object are also defined within the class. It can be said in other words that class is a template or blueprint that specifies the characteristics of some entity.
For example, the characteristics shared by all dogs are defined by the Dog class. It consists of properties such as breed and fur color and behaviors such as siting and barking ability. An object-oriented computer program gets modularity with the help of classes. The characteristics of the class must be defined in such a manner that a non programmer having knowledge about the problem should be able to recognize them. The code of the class should be also self-contained in nature. The methods and properties that make up a class are known as its members.
4) Inheritance :
Inheritance is the process of declaring and defining a new class by extending features of existing class. The extension of features is done in terms of procedures or methods and data.
With the help of inheritance the objects belonging to one class are able to get the properties of the objects belonging to another class. With the help of inheritance, code can be reused by just adding the new features to an existing class without carrying out any modification. To do this a new class has to be derived from the existing class.
5) Data Abstraction :
The process of abstraction hides all the low-level details and represents only those features that are essential. It is one of the important characteristics of an object using which the particular object can be differentiated from others. It helps in defining boundaries in a crisp manner with regard to the viewer's perspective. The prime objective of abstraction is to isolate the important aspects from the unimportant ones and suppress the later. Classes are also known as a list of abstract properties as they implement abstraction. It is possible to simplify the complex reality with the help of abstraction. This is done by designing classes that fits with the problem. Work can be also carried out at the most suitable level of inheritance based on the problem.
6) Encapsulation :
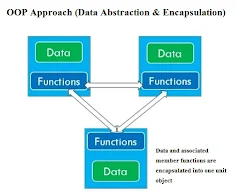
Encapsulation is defined as the process of storing data and associated functions within a single class. This process is also known as information hiding and is complimentary to abstraction. In order to create the objects both data and code are defined using this process. There are many programmers who misinterpret that encapsulation means only data hiding. However, the process hides both code and data. Some of the code and data remain restricted as private member of the object while the others can be accessed directly as interface of the object. As a practice the data members are kept private and they are accessed using the member functions of the class which are declared in the public part. Only the functions declared within the class access the data. With the help of encapsulation it is possible to hide the operational details of a class from the objects. They can communicate via messages only. The concept of encapsulation and data abstraction has been shown in figure :
7) Polymorphism :
The capability of taking multiple forms is known as polymorphism. Depending on the instance an operation may change its behavior. The behavior is based on the data type that has been used to perform the operation. In order to implement inheritance polymorphism is used extensively. Using polymorphism the programmer is able to treat the members of parent class and derived class in the same way. Polymorphism provides ability to the objects of different data types to respond to methods of same name based on some particular behavior based on a specific type. It becomes possible to abstractly use an operator like +, - or* in various situations.
8) Message Passing :
By passing messages an object can ask some other object to invoke a method or simply exchange data with each other. It is also known as interfacing in some programming languages.
Object-Oriented System Development Life Cycle
The Object-Oriented System Development Life Cycle (OOSDLC) is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. It specifically emphasizes the use of object-oriented programming (OOP) principles and techniques throughout the stages of system development. Here are the key stages in the Object-Oriented System Development Life Cycle:
1) System Planning and Feasibility Study:
- Identify the need for a new system or the need to modify an existing one.
- Conduct a feasibility study to assess the technical, economic, and organizational feasibility of the proposed system.
2) System Analysis:
- Gather and analyze requirements, typically focusing on capturing objects, classes, and their relationships.
- Use tools such as use case diagrams, class diagrams, and sequence diagrams to model system behavior and structure.
3) System Design:
- Create detailed design specifications based on the analysis phase.
- Develop class diagrams, interaction diagrams, and state diagrams to depict the structure and behavior of the system.
- Identify reusable components and design patterns.
4) Object-Oriented Implementation:
- Write code based on the design specifications, using an object-oriented programming language.
- Follow OOP principles, such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, to implement classes and objects.
- Test individual classes and methods during the implementation process.
5) Testing:
- Conduct unit testing to verify that individual classes and methods work correctly.
- Perform integration testing to ensure that classes work together as intended.
- Carry out system testing to validate the entire system against the requirements.
6) Deployment:
- Install the system in the production environment.
- Train end-users and provide documentation for system use.
- Monitor and support the system during the initial period of operation.
7) Maintenance and Evolution:
- Address bugs and issues discovered after deployment.
- Make necessary updates and enhancements based on changing requirements.
- Consider the incorporation of new technologies or features to keep the system up-to-date.
Throughout the Object-Oriented System Development Life Cycle, developers use modeling tools and diagrams to represent the system's structure, behavior, and interactions. This approach helps manage complexity, promotes code reusability, and supports the creation of systems that are scalable and maintainable. The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is often used as a standard notation for modeling during these phases.
Object Oriented System Examples
Object-oriented systems are prevalent in various domains, and many software applications and frameworks leverage object-oriented principles for their design and implementation. Here are some examples of object-oriented systems:
1) Java Standard Edition (Java SE):
Java is a widely used object-oriented programming language, and its standard edition provides a platform for developing desktop applications. Java utilizes classes and objects, and it is known for its portability and platform independence.
2) C# and .NET Framework:
C# (C Sharp) is another popular object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft. It is often used in conjunction with the .NET Framework, which is an extensive set of libraries and tools that support object-oriented development for Windows applications.
3) Python:
Python is a versatile programming language that supports both procedural and object-oriented programming. Many Python libraries and frameworks, such as Django for web development, are designed using object-oriented principles.
4) Ruby on Rails:
Ruby on Rails is a web application framework written in Ruby, a dynamic, object-oriented programming language. Ruby on Rails follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern and promotes the use of objects for building scalable and maintainable web applications.
5) Unity3D Game Development:
Unity3D is a popular game development platform that uses C# for scripting. Game development, in general, lends itself well to an object-oriented approach, where game entities, behaviors, and interactions are modeled as objects.
6) E-commerce Systems:
Many e-commerce systems are built using object-oriented principles to model products, customers, orders, and various business processes. This facilitates the creation of modular, extensible, and maintainable systems.
7) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems:
ERP systems, which integrate various business processes within an organization, often use object-oriented principles for modeling different aspects of business operations, such as inventory, finance, and human resources.
8) Simulation Software:
Object-oriented programming is commonly used in simulation software to model real-world systems. For example, in simulation games or scientific simulations, objects can represent entities like vehicles, agents, or physical elements.
9) Graphics and Multimedia Software:
Applications for graphics and multimedia, such as image editing software or video editing tools, often use object-oriented design to represent graphical elements, effects, and interactions.
10) Financial Systems:
Object-oriented principles are applied in the development of financial systems to model entities like accounts, transactions, and financial instruments, allowing for a flexible and modular design.