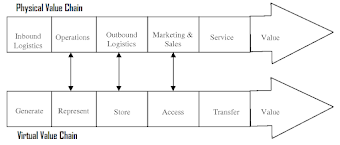
The concept of virtual value chain (VVC) is very similar to the physical value chain. It comprises the digital, networked and virtual realm of information. The concept of the virtual value chain was created (propounded) by Jeffrey Rayport and John Sviokla. The virtual part of VVC indicates that all value creation is done through information. The creation of value in the VVC happens through the following five steps :
Virtual Value Chain Stages :
Gathering → Organizing → Selection → Synthesis → Distribution
By completing these five steps the organisation is able to create new markets for its products and also redefine the existing relationships in its product markets. The value creation aspect in the Virtual Value Chain happens through the exchange of information over the organization's network. It does not involve any direct exchange of products and services like the traditional value chain. The VVC converts raw information into digital products.
Figure signifies a number of things. First, it shows that the process of value creation in a virtual value chain is very similar to the physical value chain. The same process is followed for both. Second, the increasing importance of information in an organisation indicates that the VVC can be thought of as being higher in the hierarchy compared to the physical value chain.
For example (Virtual Value Chain Example), the virtual value chain may suggest changes in the physical value chain. This leads to a third paint that the virtual value chain is complementary in nature to the physical value chain. It should not be considered as a replacement of the latter.
Figure : New Value Chain :
The scope of virtual value chain is limited to information processes. For other processes, the organisation utilizes the output of VVC to complement the physical value chain. This creates a competitive advantage for the organisation if the linkages are harnessed properly.
Objectives of Virtual Value Chain
The virtual value chain has the following objectives :
- Creating direct cost-effective interactions among value chain members and customers.
- Giving end-user customers with particular value service advantages on matters like performance, looks and aesthetics, security aspects, reliability, economy, etc.
- To ensure that value is created and delivered on a continuous basis.
Principles of Virtual Value Chain
1) Law of Digital Assets :
Digital assets, unlike physical ones, are more durable in nature. Organizations can therefore use and reuse their digital assets as many times as they want. This has major cost advantages for the company.
For example, the cost of utilizing digital assets is practically close to zero. As a result a company which utilizes digital assets will have a much lower cost structure than one which uses traditional assets to create value. Companies utilizing digital assets can thus price their products at very low price and still make profits. This will not be possible for the company using traditional assets.
2) New Economies of Scale :
Since the cost of digital assets is very less the company utilizing these assets can achieve economies of scale even at much lesser volumes. It is thus possible for a smaller company to compete against much larger companies if it utilizes digital assets in creating value.
3) New Economies of Scope :
The company can also have economies of scope as the same digital asset can be used to create vale across different markets and product categories.
4) Transaction-Cost Compression :
The transaction costs of the VVC are also much lower than the physical value chain. Also the transactions in virtual value chain keep on increasing as the processing capacity of microprocessors per unit of cost also doubles every eighteen months.
5) Re-balancing Supply and Demand :
Businesses these days are rapidly changing from a "supply side orientation to a "demand side orientation". The emphasis is on knowing the needs and desires of the customers and responding to them than on merely making products and services. This is possible only if the company gathers, collects and analyses the information in the market place.
Relevance of Virtual Value Chain / Advantages of Virtual Value Chain
1) Inbound Logistic-Efficient Transport and Logistics Management :
The use of internet technologies will bring in greater efficiency in the transport and logistics management of products and services. These technologies will help the physical value chain by providing real time information on the products arrival. The information includes the delivery of raw materials to manufacturers, the delivery to distributors and from there to retailers and finally purchases by customers. The availability of real time information will help the manufacturers and retailers to plan their transport and logistics requirements more effectively. There will be less wastage in the system and also accompany in better warehousing and storage mechanisms.
2) Operations :
The manufacturers can employ mass customization to customize the products and services to large clusters of customers who have similar needs.
For example, the design of a cleaning detergent that addresses the need of a particular workplace, pesticides which are tailored to the insect density of a particular location, cosmetics and beauty care products which have been designed to prevent exposure to a particular allergen or chemical.
3) Outbound Logistics :
Packaging constitutes a large part of the manufacturing cost of an organisation. The environmental impact of packaging is immense as it leads to the creation of solid waste. Internet based technologies use innovative packaging options. The use of pollution causing packaging can be avoided.
4) Marketing and Sales :
The website is also a source of communication of information to customers, manufacturers and the environment. The organisation can display its merchandise online and does not need the presence of a physical building or display zone. The organisation can use the website to communicate with all its stakeholders.
5) Service and Support :
The internet also provides the company with a medium to remain in touch with customers after they have made their purchase. When an online purchase is made, the company gets access to information like telephone number, mobile, email, address, demographics etc. The company can use this Information to remain in touch with the customer after he has made his purchase. The internet thus also serves as a very good medium to share information on product usage and safety norms, product recall information, options for selling and disposal etc.
6) Technology Development :
The internet is also leading to the growth of flexi and at-home work options. More and more employees are opting for these working conditions. While this will definitely increase electricity consumption at homes, but it will reduce the need for more office space and lesser utility bills and also reduced travelling by employees.
7) Procurement :
The internet has also crashed the time required for procurement. In the traditional set up procurement is a very time consuming manual process. It is a very subjective process and lacks transparency. By standardizing the procurement process and making it electronic, the internet has brought in major improvements in this regard. The growth of Business to business marketplaces has also brought in greater efficiency in this process.
For example, the rapid growth of indiamart.com in India is a point. Indiamart.com is a business to business marketplace which caters to the procurement needs of the SME.
8) Customer Relations :
The internet is also a source of information for the needs and attitudes of customers. Organizations use this information to create value in their product and service offerings. The internet also disseminates product information electronically through e-catalogues. This can be used by forums and discussion groups to discuss the product and its features.
Difference between Virtual Value Chain and Physical Value Chain
From table we can see the virtual value chain is different from the physical value chain in many respects. Table compares the virtual value chain and the physical value chain on the economy principle, management content, process of value increment, information effect, etc.
|
Comparison
Item |
Physical Value Chain |
Virtual Value Chain |
|
1) Economy Principle |
Reduction
of marginal profit |
Increase
of marginal profit |
|
2) Management Content |
The product is real and
tangible |
The
product is digital and intangible |
|
3) Process of Value
Increment |
The
action is continuous |
Action
is discontinuous |
|
4) Information Effect |
Is an assistant to main
physical process |
Is used to create value |
|
5)
Agency |
The
agency is physical |
The agency is intangible
i.e. information agency |
|
6) Role of Clients |
Acceptors of products and
services |
Participate
in creating or producing |
|
7) Focus |
Manufacture, service and
creation of value |
Creating
value through information |